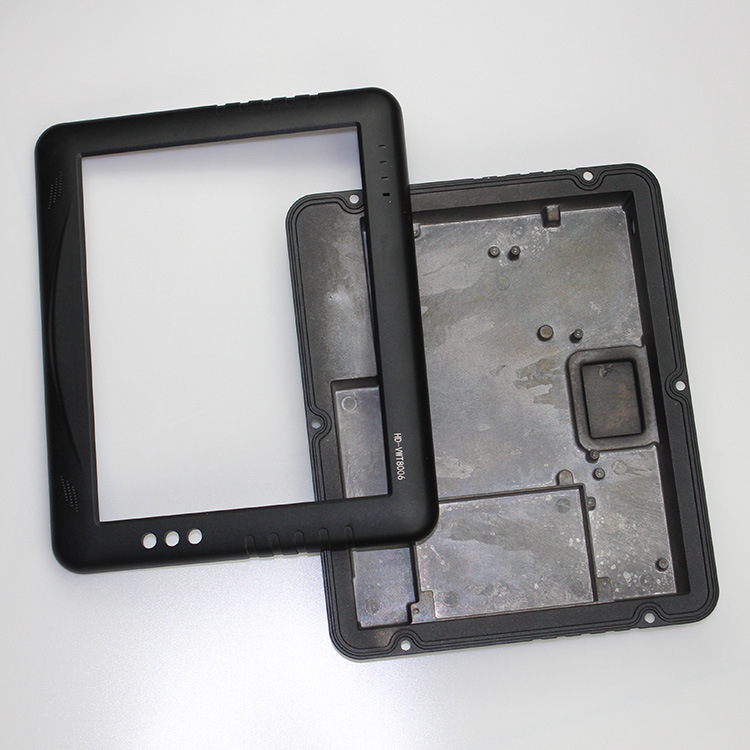
Crafting the Perfect Car Display Back Cover: The Intricacies of Thin-Walled Aluminum Die Castings
The automotive industry continuously seeks innovative solutions to enhance vehicle performance and aesthetics. One crucial component that often goes unnoticed is the car display back cover. These covers protect delicate electronics and contribute to the overall look and feel of the vehicle's interior.
This blog post will explore the sophisticated production process of thin-walled aluminum die castings for car display back covers. We'll explore cutting-edge technologies, such as aluminum die casting, CNC machining, threading, polishing, and painting. Additionally, we'll discuss the selection of ADC 12 aluminum alloy, the importance of surface finishes, and the challenges faced during production. By the end of this article, you'll gain a deeper appreciation for the engineering prowess behind these essential automotive components.
Manufacturing Technology Overview
Aluminum Die Casting
Aluminum die casting is a manufacturing process where molten aluminum is injected into a steel mold under high pressure. This highly efficient method produces parts with excellent dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finishes. Aluminum, particularly ADC 12, is preferred in automotive applications due to its lightweight properties, high corrosion resistance, and superior mechanical strength. ADC 12 alloy is known for its excellent castability. It is ideal for creating complex, thin-walled components like car display back covers.
CNC Machining
Once the aluminum die-casting process is complete, the parts often require further refinement to meet precise specifications. It is where CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining comes into play. CNC machining allows for high precision in cutting, drilling, and shaping the die-cast parts. It ensures that the car display back covers meet exact tolerances, which is crucial for components fitting perfectly within the vehicle's dashboard. The precision of CNC machining helps achieve consistent quality and reliability in the final product.
Threading, Polishing, and Painting
To enhance the functionality and aesthetics of the car display back cover, additional finishing processes are employed:
Threading: This process involves creating screw threads on the die-cast parts. Threading is essential for assembly, allowing the back cover to be securely attached to other components.
Polishing: Polishing is a critical step in achieving a smooth, reflective surface on the aluminum parts. It involves mechanically buffing the surface to remove any imperfections, resulting in a high-gloss finish that enhances the appearance of the car display back cover.
Painting: Painting not only improves the visual appeal of the back cover but also provides a protective layer against corrosion and wear. The painting process typically involves applying a primer, base coat, and clear coat to ensure durability and a high-quality finish.
Die Cast Material Selection
ADC 12 Alloy
ADC 12 is an aluminum alloy widely used in the die-casting industry, particularly for automotive applications. This section will explore the critical properties of ADC 12 and why it is the preferred choice for manufacturing car display back covers.
Properties of ADC 12:
Excellent Castability: ADC 12 has a low melting point and fluidity, making it easy to cast into intricate shapes and thin-walled structures. It is crucial for producing detailed, lightweight components like car display back covers.
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: One of the standout properties of ADC 12 is its high strength relative to its weight. It makes it ideal for automotive applications where reducing weight without compromising strength is essential.
Good Corrosion Resistance: ADC 12 exhibits excellent resistance to corrosion, which is vital for automotive components exposed to various environmental conditions. It ensures longevity and reliability in the final product.
Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum alloys, including ADC 12, have good thermal conductivity, which helps dissipate heat generated by electronic components housed within the display back cover.
Dimensional Stability: ADC 12 offers good dimensional stability, meaning it maintains its shape and size under various conditions, which is critical for parts that must fit precisely within an assembly.
Why ADC 12 is Chosen for Car Display Back Covers: The automotive industry demands materials that meet stringent performance and safety standards. ADC 12's castability, strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity make it ideal for car display back covers. These covers must be lightweight to improve overall vehicle efficiency while providing robust protection for sensitive electronic displays.
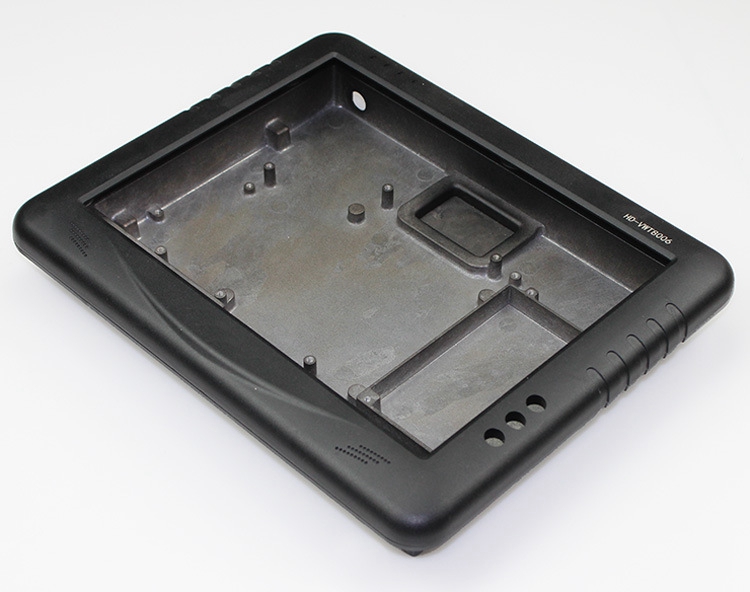

Performance Benefits in the Automotive Environment:
Weight Reduction: Using ADC 12 helps reduce the vehicle's overall weight, contributing to better fuel efficiency and lower emissions.
Durability: The inherent strength and corrosion resistance of ADC 12 ensure that the display back covers can withstand the rigors of daily use and harsh environmental conditions.
Heat Management: The good thermal conductivity of ADC 12 aids in managing the heat generated by the display electronics, preventing overheating and extending the lifespan of the components.
Aluminum Die Castings Surface Finish
Polishing
Polishing is critical in producing car display back covers, mainly when dealing with thin-walled aluminum die castings. The goal of polishing is to create a smooth, reflective surface that enhances the appearance and functionality of the part. Here's a closer look at the techniques used and their importance:
Techniques Used in Polishing Thin-Walled Die Castings:
Mechanical Buffing: This involves using abrasive materials to buff the surface of the aluminum part. Mechanical buffing smooths out any rough spots or imperfections that may have resulted from the die-casting process.
Electrolytic Polishing: Electropolishing uses an electrolytic bath to remove a thin layer of the metal, further smoothing the surface and enhancing its reflective properties. This method is beneficial for achieving a high-gloss finish on complex geometries.
Vibratory Polishing involves placing the parts in a vibratory machine filled with abrasive media. The vibration causes the media to gently polish the surface, which is especially effective for parts with intricate shapes or difficult-to-reach areas.
Achieving a Smooth and Reflective Surface: Polishing not only improves the visual appeal of the car display back cover but also enhances its functionality. A smooth surface reduces friction and wear, prolonging the part's life. Moreover, a reflective surface can improve the overall aesthetics of the vehicle's interior, providing a premium look and feel.
Painting
Painting is the final step in the finishing process. It is crucial in protecting and beautifying the car display back cover. Here's an in-depth look at the painting process and its significance:
Types of Paints and Coatings Used:
Primer: The primer layer serves as the foundation for the paint job. It enhances adhesion, fills minor imperfections, and provides a uniform surface for the subsequent layers.
Base Coat: This is the primary color layer. Automotive-grade paints are used for the base coat to ensure durability and an attractive finish. The choice of color and type of paint can vary depending on the desired aesthetic and performance requirements.
Clear Coat: The final layer is the clear coat, which protects against environmental factors such as UV rays, moisture, and chemicals. It also gives the part a glossy finish, enhancing its appearance.
The Painting Process and Its Importance:
Surface Preparation: Before painting, the surface of the aluminum part is thoroughly cleaned and prepared to ensure optimal paint adhesion. It may involve degreasing, sanding, and applying a primer.
Application: The paint is typically applied using spray techniques to ensure an even and consistent coat. Each layer (primer, base coat, and clear coat) is applied and cured before the next layer is added.
Curing: After the paint is applied, the part undergoes a curing process, heating to a specific temperature to harden the paint. This step is crucial for achieving a durable and resilient finish.
Protective and Aesthetic Benefits: Painting enhances the visual appeal of the car display back cover and provides essential protection. The paint layers protect the aluminum from corrosion, scratches, and other environmental damage. Additionally, a high-quality paint job can significantly enhance the perceived value of the vehicle, contributing to a better overall customer experience.
Challenges in Aluminum Die Casting
Thin-Wall Die Casting
Thin-wall die casting presents unique challenges due to maintaining structural integrity while producing lightweight components. Here are some of the primary difficulties and their solutions:
Technical Difficulties:
Maintaining Uniform Wall Thickness: Achieving consistent wall thickness in thin-walled castings is critical to prevent weak spots and ensure structural integrity. Variations can lead to defects such as warping or cracking.
Mold Filling: Ensuring that the molten aluminum fills the mold entirely and evenly is more challenging with thin walls. Incomplete filling can result in defects and weak points in the final product.
Solutions:
High-Precision Molds: High-precision molds with tight tolerances help achieve uniform wall thickness and consistent quality.
Optimized Casting Parameters: Adjusting the casting parameters, such as injection speed and pressure, to ensure complete and even filling of the mold. Using simulation software to optimize these parameters can also be beneficial.
Alloy Selection: Choosing a suitable aluminum alloy, like ADC 12, which has excellent fluidity, helps achieve better mold filling and thin-walled structures.
Die Cast Cold Shrink and Deformation
Cold shrink and deformation are common issues in die casting, especially for thin-walled parts. These defects can compromise the functionality and appearance of the final product.
Causes:
Rapid Cooling: Thin-walled sections are faster than thicker sections, leading to differential cooling rates and potential shrinkage.
Residual Stresses: Stresses built up during casting can cause deformation as the part cools and solidifies.
Methods to Mitigate These Issues:
Controlled Cooling: Implementing controlled cooling processes ensures uniform cooling rates throughout the part. It can involve using cooling channels within the mold to regulate temperature.
Heat Treatment: Applying post-casting heat treatment processes like annealing to relieve residual stresses and stabilize the part dimensions.
Design Optimization: Optimizing the part's design to minimize areas prone to shrinkage and deformation. It can involve using ribbing or gussets to reinforce thin-walled sections.
Case Study: Real-Life Example
Let's look at a real-life example to illustrate these challenges and solutions.
Scenario: A major automotive manufacturer needed a thin-walled aluminum die-cast back cover for their new car display unit. The requirements included
maintaining a uniform wall thickness of 1.5mm,
achieving a high-gloss finish, and
Ensuring the part could withstand environmental stresses.
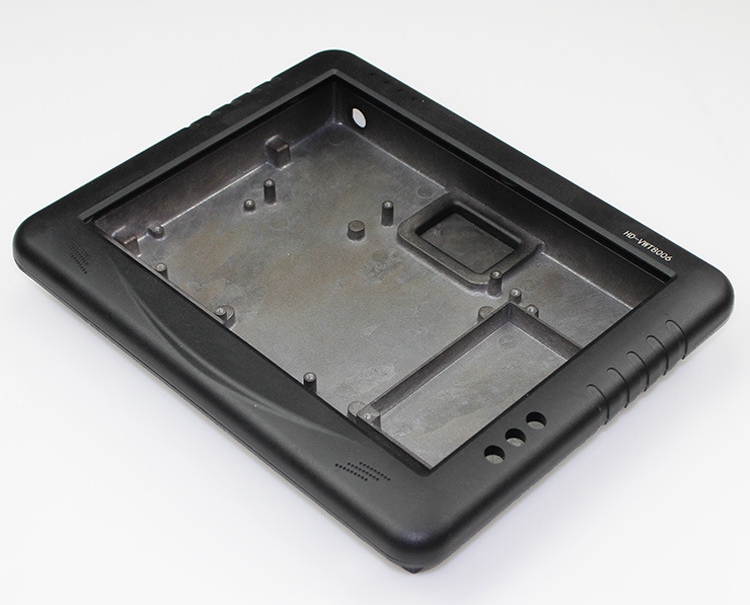

Challenges Encountered:
Inconsistent Wall Thickness: Initial prototypes exhibited variations in wall thickness, leading to structural weaknesses.
Cold Shrinkage: Rapid cooling resulted in shrinkage defects, causing dimensional inaccuracies.
Deformation: Residual stresses led to deformation during the cooling process, affecting the fit and finish of the part.
Solutions Implemented:
Precision Molding: The manufacturer used high-precision molds with optimized gating systems to ensure uniform wall thickness.
Optimized Cooling: Controlled cooling was implemented using advanced cooling channels within the mold, ensuring uniform cooling rates and minimizing shrinkage.
Post-Casting Heat Treatment: Annealing processes were applied to relieve residual stresses, reducing deformation and stabilizing dimensions.
Outcome: The final product met all the specifications, with uniform wall thickness, no shrinkage defects, and excellent dimensional stability. The high-gloss finish was achieved through meticulous polishing and painting, resulting in a visually appealing and durable car display back cover.
What We Can Do In Diecasting?
Producing high-quality car display back covers involves a complex interplay of advanced manufacturing technologies, material selection, and meticulous finishing processes. Manufacturers can achieve functional and aesthetically pleasing components by leveraging the strengths of aluminum die casting, CNC machining, threading, polishing, and painting.
Key Takeaways:
Advanced Technology Integration:
Combining aluminum die casting and CNC machining ensures precision and consistency in producing thin-walled components.
Threading, polishing, and painting are essential finishing steps that enhance the final product's functionality and appearance.
Material Advantages:
ADC 12 aluminum alloy is the material of choice for its excellent castability, high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and thermal conductivity.
These properties make ADC 12 ideal for automotive applications, where performance and durability are critical.
Overcoming Production Challenges:
Thin-wall die casting presents unique challenges that can be addressed through high-precision molds, optimized casting parameters, and controlled cooling techniques.
Mitigating issues like die-cast cold shrink and deformation requires a combination of design optimization and post-casting treatments.
Importance of Surface Finish:
Polishing and painting processes are crucial for achieving a smooth, reflective surface and providing protective layers against environmental factors.
A high-quality surface finish enhances the visual appeal and longevity of the car display back cover.
Real-World Application:
The case study highlights the practical application of these technologies and processes, demonstrating how challenges can be overcome to produce superior automotive components.
The successful production of car display back covers showcases the importance of precision, innovation, and quality control in manufacturing.
Future Trends in Thin-Walled Die Casting for the Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is poised to see further advancements in thin-walled die casting and related manufacturing processes. Innovations such as enhanced simulation software, improved material formulations, and automated finishing techniques are expected to drive even higher standards of quality and efficiency.
Potential Developments:
Enhanced Simulation and Process Control: Continued improvements in simulation tools will allow for better prediction and control of casting parameters, leading to reduced defects and higher consistency.
New Material Innovations: Research into new aluminum alloys and composite materials could offer better performance characteristics, such as increased strength and improved thermal properties.
Automation in Finishing Processes: Automation and robotics in polishing, painting, and other finishing processes will enhance precision, reduce manual labor, and increase production speed.

