What Materials Can Nway Work With for Rapid Prototyping Service?
Neway offers a wide range of materials to suit rapid prototyping needs across plastics, metals, and resins. Choosing a suitable material is critical to achieving the desired aesthetics, functionality, mechanical properties, and simulation of production parts.
Plastics for FDM 3D Printing
Fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printing uses production-grade thermoplastics heated through a nozzle to build prototypes layer by layer. Common materials include:

ABS – Strong, durable plastic with temperature resistance. Used for functional prototypes and end-use parts.
PLA – Biodegradable polymer made from renewable resources. More limited strength than ABS but is easier to print.
PETG – PET plastic with added glycol for enhanced flexibility and impact resistance.
TPU and TPE – Flexible, rubber-like materials for elastic components and functional prototypes.
PC – Polycarbonate has very high strength and temperature resistance for demanding applications.
ASA – UV-stable polymer for prototyping outdoor applications. It offers acrylic-styrene properties.
FDM materials provide an affordable option for concept models, form and fit testing, jigs, and fixtures. Available colors include natural transparent or opaque tones and primary colors like black and white.
Resins for Stereolithography (SLA)
Stereolithography uses UV lasers to selectively cure liquid plastic resin into solid 3D parts with delicate features and a smooth surface finish. SLA resins include:
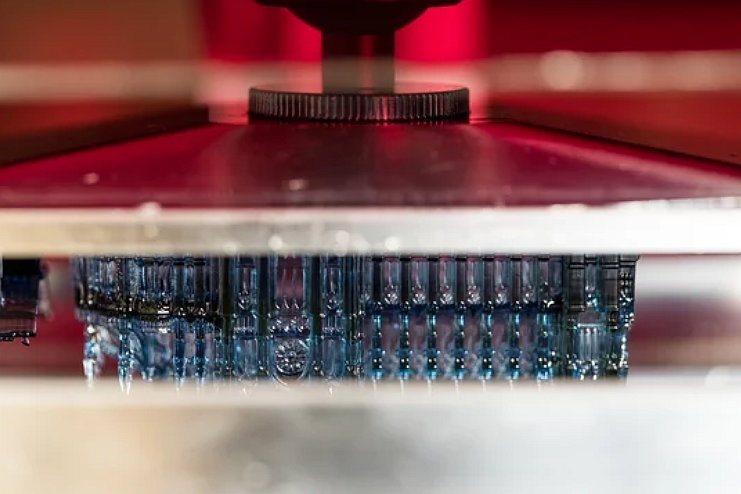
Standard – General purpose photopolymers with properties similar to ABS plastic.
Durable – Tougher, high-strength resins resistant to heat and moisture.
Flexible – Elastic-like resins for living hinges, snap fits, and rubber components.
Castable – Burn-out materials for investment casting of complex metal parts.
Dental – Biocompatible resins for modeling dental applications.
Engineering – Advanced resins like Accura 60 simulate polypropylene properties.
SLA offers high accuracy and detail for form and fit prototypes. The liquid resin system enables intricate geometries not feasible with other processes.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) Materials
SLS utilizes a laser to fuse powdered material, layer by layer, into finished 3D parts inside a build chamber. SLS materials include:
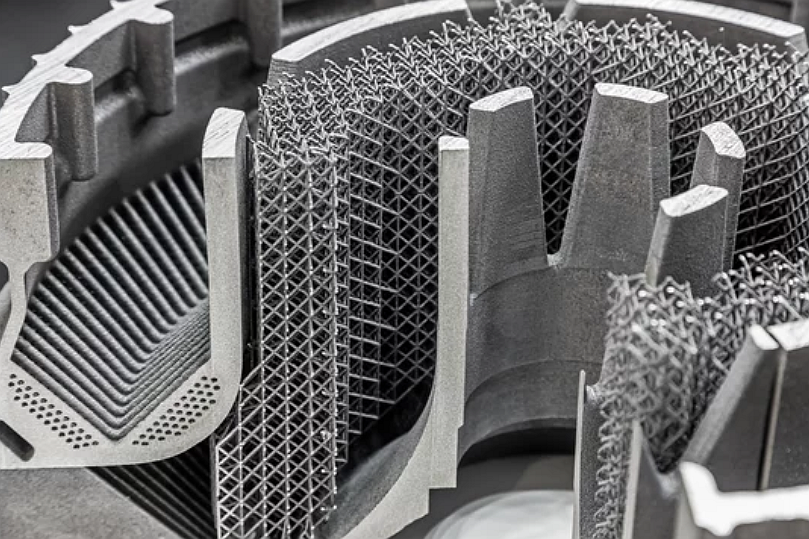
Nylon (PA) – Most common SLS material with strength, flexibility, and surface quality.
Glass-filled Nylon – Nylon reinforced with glass beads for 40% higher rigidity and improved dimensional stability.
Alumide – Nylon and aluminum composite with enhanced stiffness and heat resistance.
TPU Elastomer – Flexible polyurethane powder suitable for elastic components.
PEBA – Rubber-like SLS material ideal for applications requiring softness and flexibility.
SLS produces durable prototypes mimicking engineered plastics like ABS, polypropylene, and acetal. Material properties can also be tuned by varying laser parameters.
Photopolymer Resins for PolyJet 3D Printing
PolyJet 3D printing jets tiny droplets of liquid photopolymer onto a build tray instantly cured by UV light. Mixing ratios of rigid and elastomeric polymers enable different material properties. Common resins include:
Vero Series – Rigid opaque materials in different shades from gray to clear.
Tango Series – Rubber-like flexible and transparent polymers.
Digital ABS – Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene-like resins. Heat resistance to 85°C.
Transparent & Clear Resins – Optically clear materials for lighting effects and see-through parts.
Biocompatible – Medical-grade certified materials for biocompatible applications.
Polyjet provides an exceptionally smooth surface finish and complexity like overhangs without supports. The physical properties closely match standard plastics.
Metals for Additive Manufacturing
Selective laser melting (SLM), direct metal laser sintering (DMLS), and other powder bed fusion methods melt fine metallic powders into finished metal parts layer by layer. Metals include:
Stainless Steel – The most widely used metal for functional metal prototypes and end-use parts.
Aluminum Alloys – Lightweight but strong alternatives to steel for aerospace and automotive.
Titanium – Extremely durable, low-weight biocompatible metal popular for medical implants.
Nickel Alloys – Corrosion and heat-resistant alloys like Inconel are common in aerospace.
Tool Steels – Hardened tool steel grades up to 62 HRC for dies, molds, and tooling.
Precious Metals – Gold, silver, and platinum jewelry alloys.
Binder jetting and directed energy deposition are other additive technologies suitable for large metal parts. The layered metal fuses into fully dense, functional prototypes.
CNC Machining Metals and Plastics
Computer numerical control (CNC) machining prototyping service is a subtractive process of removing material using cutting tools. Common materials include:
Aluminum – Lightweight, corrosion-resistant metal available in a variety of alloys.
Brass and Copper Alloys – Denser non-ferrous metals with electrical/thermal properties.
Tool Steels – Hardened steel for high wear resistance and strength.
Stainless Steel – Rust-resistant steel is available in different grades.
Titanium – Light but solid and biocompatible exotic metal.
Engineering Thermoplastics – Machinable nylon, acetal, PEEK, ABS, and polycarbonate grades.
CNC machining produces functional metal and plastic prototypes that withstand rigorous testing for concept validation.
Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet metal cutting and forming prototyping services shape thin raw materials into finished parts. Typical sheet metals:
Aluminum – Lightweight metal available in sheet, plate, and foil.
Steel – Most common sheet metal. Carbon steel or stainless steel.
Copper – Ductile, conductive metal used for electronics enclosures.
Brass – Corrosion-resistant copper alloy.
Titanium – Light but very strong and corrosion-resistant.
Sheet metal offers rapid prototyping of enclosures, plates, brackets, and complex assemblies. Parts can be welded or mechanically fastened.
Injection Molding and Other Molding Materials
Rapid injection molding with 3D printed molds uses a wide range of thermoplastics:
ABS – Strong engineering plastic used across consumer products.
Nylon (PA) – Tough, durable engineering thermoplastic.
PC – A very rigid plastic with high heat and impact resistance.
PP – Soft, flexible polypropylene plastic.
POM – Acetal is a stiff plastic used for precision parts.
TPU – Flexible, rubber-like thermoplastic polyurethane.
Rapid tooling for thermoforming and vacuum casting also produces prototypes from sheet plastics:
ABS
HIPS
Polycarbonate
PETG
Acrylic
The right material choice allows parts to mimic end products' mechanical properties, appearance, and performance.
In summary, Neway offers an extensive material selection across plastics, resins, and metals to meet varying application requirements for stiffness, strength, heat resistance, flexibility, and functionality.



