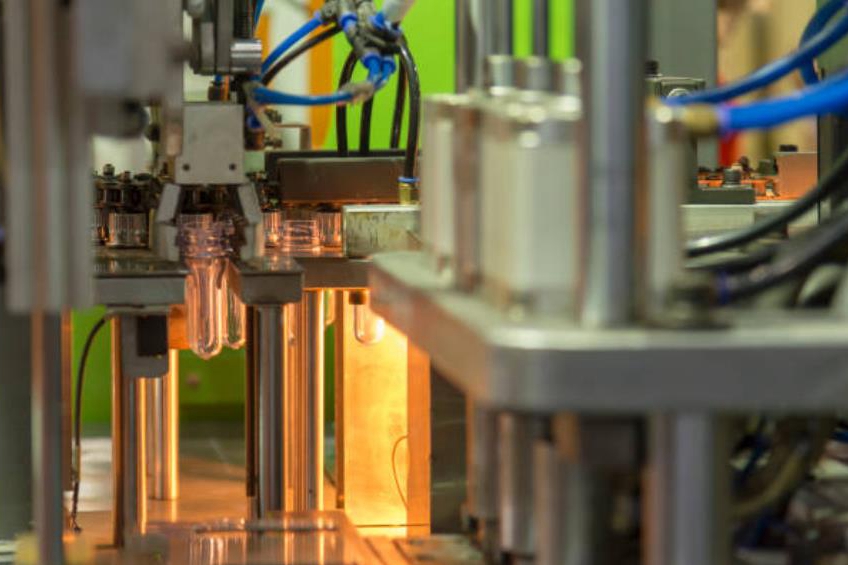
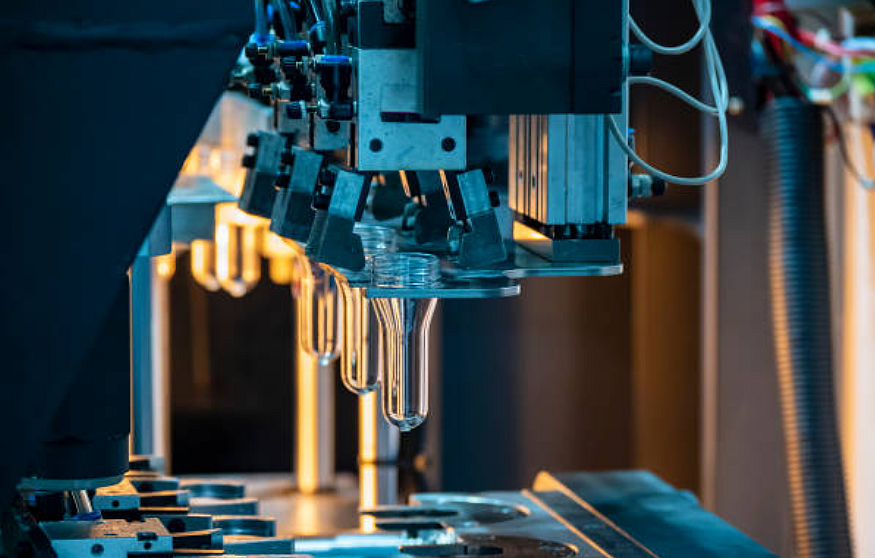
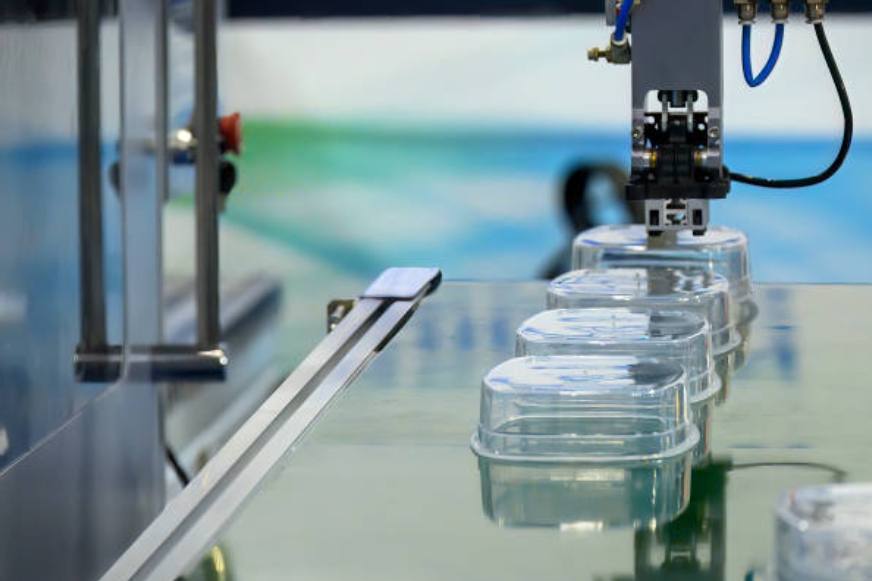
PPO
PPO Injection Molding Service
Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic known for its exceptional dimensional stability, heat resistance, and electrical insulating properties. Chemically, PPO is distinguished by its aromatic ether backbone, which contributes to its high thermal stability and low moisture absorption. This plastic offers a unique combination of properties, making it ideal for demanding applications across various industries.
Critical Properties of PPO:
High Heat Resistance: PPO can withstand continuous exposure to high temperatures, maintaining its structural integrity and performance without significant degradation.
Excellent Dimensional Stability: The material exhibits minimal shrinkage and low thermal expansion, ensuring that components maintain their precise dimensions even under thermal stress.
Low Moisture Absorption: PPO's resistance to water absorption helps maintain its mechanical properties and dimensional stability in humid environments, making it suitable for applications where consistent performance is critical.
Good Electrical Insulation: With its excellent dielectric properties, PPO is frequently used in electrical and electronic applications for parts that require good insulation.
Chemical Resistance: PPO is resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, bases, and detergents, which makes it suitable for use in harsh chemical environments.
Common Applications of PPO:
Electrical and Electronics Industry: Used in components like connectors, coil forms, and parts of household appliances where good electrical insulation is required.
Automotive Sector: Due to its heat resistance and mechanical stability, PPO is used in automotive parts exposed to high temperatures, such as under-hood components.
Medical Devices: Its biocompatibility and stable properties make PPO suitable for specific medical device applications, where sterilization and durability are essential.
Consumer Goods: PPO is also used in various consumer goods, including kitchen appliances and structural parts, where durability and aesthetics are essential.

Chemical Composition of injection molding PPO plastic
Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO), also known as Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide), is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic characterized by a unique chemical structure contributing to its desirable properties. PPO's chemical composition and structure are crucial in its performance, especially in injection molding applications.
Chemical Structure:
PPO is a polymer made up of repeating units derived from 2,6-dimethylphenol. The key structural element of PPO is the phenylene group (a benzene ring), which is linked by ether bonds (an oxygen atom between two carbons). This structure contributes to the polymer's high thermal stability and low moisture absorption.
Key Features of PPO's Chemical Structure:
Aromatic Backbone: An aromatic (benzene) ring provides high rigidity and strength. The aromatic nature of PPO also contributes to its excellent thermal stability, allowing the polymer to maintain its properties at higher temperatures than many other thermoplastics.
Ether Linkages: The oxygen atoms in the ether linkages between the phenylene groups enhance the flexibility of the polymer chain while also contributing to its overall heat resistance. These linkages reduce the tendency of the polymer chains to pack tightly, lowering the density of the material and enhancing its insulating properties.
Methyl Substituents: The methyl groups attached to the benzene rings increase the hydrophobicity of the polymer, which significantly reduces its moisture absorption. This feature is crucial for maintaining PPO's electrical and mechanical properties in humid environments.
Chemical Resistance:
The unique structure of PPO makes it resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, bases, and many solvents. This resistance is mainly due to the stability of the aromatic and ether components, which do not readily react with most chemicals.
Blending with Other Polymers:
PPO is blended with polystyrene (PS) and other polymers to improve its processability and impact strength in many commercial applications. These blends are more accessible to process via injection molding. They are used to produce various complex parts and components. The blending often involves adding flame retardants, impact modifiers, and other additives to achieve specific property enhancements.
Injection Molding Considerations:
When injection molding PPO, it's essential to consider the polymer's tendency to oxidize at high temperatures. Thus, stabilizers are often added to prevent degradation during processing. Additionally, due to its inherent stiffness and brittleness, impact modifiers may be included in the formulation to improve the toughness of the final product.
Physical Properties of PPO Plastic
Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) is widely regarded for its exceptional physical properties, making it a favored material in various high-demand applications, especially in electronics, automotive, and healthcare industries. Here's a detailed look at the significant physical properties of PPO when used in injection molding processes:
1. Thermal Properties:
High Glass Transition Temperature (Tg): PPO generally has a Tg of around 210°C, which provides excellent thermal stability. This high transition temperature ensures the material maintains its mechanical properties at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for applications near engines or other heat-generating components.
Low Thermal Expansion: PPO exhibits lower thermal expansion than many other plastics, contributing to its excellent dimensional stability under thermal stress.
2. Mechanical Properties:
High Strength and Stiffness: PPO is inherently strong and stiff, which makes it suitable for structural applications that require robust performance.
Impact Resistance: Though PPO is rigid, its impact resistance is moderate and can be significantly improved by blending it with other polymers, such as high-impact polystyrene (HIPS), or adding rubber modifiers.
Creep Resistance: PPO has good creep resistance, meaning it does not deform significantly under mechanical stress over time, which is critical for maintaining the integrity of mechanical parts under constant load.
3. Electrical Properties:
Excellent Electrical Insulation: PPO has outstanding dielectric properties, including high electrical resistivity and low dielectric constant, making it ideal for electronic components and electrical insulation applications.
4. Moisture and Chemical Resistance:
Low Moisture Absorption: PPO absorbs very little moisture, which helps maintain its mechanical and electrical properties in humid conditions.
Chemical Resistance: It is resistant to many chemicals, including weak acids and bases, detergents, and various solvents, making it suitable for harsh chemical environments.
5. Density:
Low Specific Gravity: Typically around 1.06 g/cm³, lower than many other engineering thermoplastics. This lower density can be advantageous for applications where weight reduction is critical.
6. Optical Properties:
Inherent Opacity: Pure PPO is naturally opaque but can be made more transparent through modifications or blending with other materials like polystyrene. Such modifications are useful for applications requiring transparency, chemical resistance, and high thermal stability.
7. Surface Properties:
Surface Finish: PPO can achieve a good surface finish, which can be glossy depending on the mold design and processing conditions. It makes it attractive for visible components in consumer electronics and automotive interiors.
8. Processing Characteristics:
Processing Temperatures: PPO processes at higher temperatures due to its high Tg. Typically, the melt temperature ranges from 280°C to 330°C, and mold temperatures are kept around 100°C to 150°C.
Shrinkage: PPO exhibits lower shrinkage rates than other thermoplastics, typically about 0.5% to 0.7%, contributing to its excellent dimensional stability in molded parts.
Considerations In PPO Injection Molding
Injection molding with Polyphenylene Oxide (PPO) requires careful consideration of several factors to leverage its beneficial properties fully while managing its unique challenges. Here are vital considerations to keep in mind when working with PPO in injection molding processes:
Material Preparation
Drying: PPO must be thoroughly dried before processing to prevent moisture-related defects such as splay marks or hydrolytic degradation. A dehumidified dryer should typically dry PPO at 120°C for 3 to 4 hours.
Handling: Keep the material protected from environmental exposure to prevent it from reabsorbing moisture and ensure cleanliness, which is critical for maintaining the quality of the final product.
Machine Requirements
Machine Type: Given PPO's high melting temperature, ensure that the injection molding machine can reach and precisely control these higher temperatures without degrading the material.
Screw Design: Utilize a screw that provides gentle melting and homogeneous mixing. PPO benefits from screws with a lower compression ratio, which minimizes shear heat and potential degradation.
Mold Design
Mold Temperature: Proper mold temperature control is essential. PPO typically requires a mold temperature between 100°C and 150°C to balance flowability and cooling time best.
Venting: Adequate venting is crucial due to PPO's high viscosity. Proper vent placement and size help prevent burns and ensure a complete fill by allowing gases to escape.
Process Parameters
Injection Temperature: PPO is processed at higher temperatures, usually between 280°C and 330°C. Optimal temperature settings depend on specific material grades and part design.
Injection Pressure and Speed: High injection and moderate speeds are recommended to fill the mold effectively while minimizing shear stress and potential flashing.
Holding Pressure and Time: Adjust the pressure and time to minimize sink marks and volumetric shrinkage, ensuring dimensional accuracy and surface aesthetics.
Post-Molding Considerations
Cooling Time: PPO parts should be adequately cooled in the mold to reduce residual stresses and warpages. However, overly prolonged cooling can lead to inefficiencies and higher cycle times.
Ejection: Given PPO's stiffness, ensure that ejection mechanisms are designed to smoothly release the part without causing stress or deformation.
Special Processing Techniques
Blending with Other Polymers: Blending PPO with materials like polystyrene can enhance its processability and impact strength. Each blend will have unique processing parameters that need to be determined experimentally.
Additives and Fillers: Utilizing stabilizers, flame retardants, or reinforcing fibers (like glass fibers) can improve PPO's properties but may require adjustments in processing conditions to accommodate changes in flow characteristics and thermal stability.
Quality Control
Dimensional Stability: Constant monitoring is necessary to ensure that parts meet dimensional specifications, mainly because PPO exhibits low shrinkage and high dimensional stability.
Surface Quality: Regular checks for aesthetic defects such as weld lines, splay marks, or sink marks are critical, as these are indicative of processing parameter imbalances.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Handling and Storage: Ensure PPO is handled safely and stored in conditions that prevent degradation or contamination.
Recycling: Consider the recyclability of PPO and PPO blends within your production cycle to enhance sustainability efforts.
What We Can Do In Injection Molding
Neway offers a variety of injection molding process options, including:
1. Plastic Injection Molding Service
4. Multi Shoot Injection Molding Service
And various standard and custom materials for injection molding, including:
Thermoplastics | Thermosets | |||
Medical-Grade silicone rubber | ||||
Optical silicone rubber | ||||



