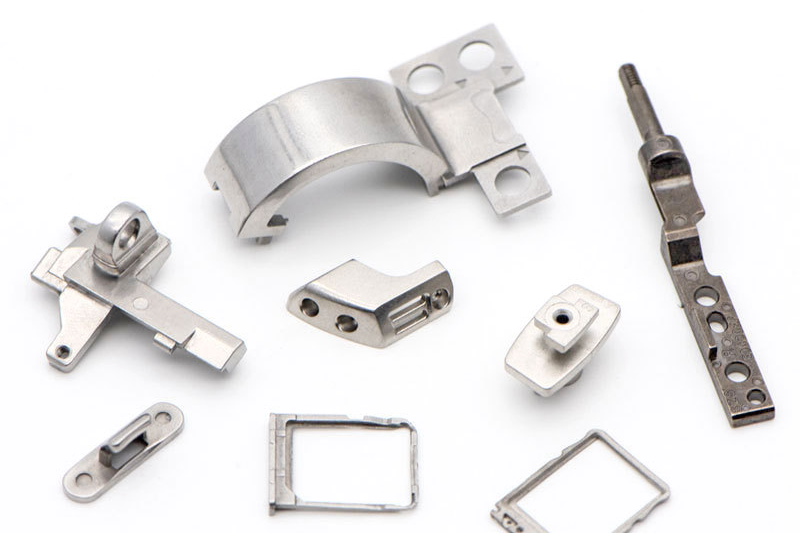
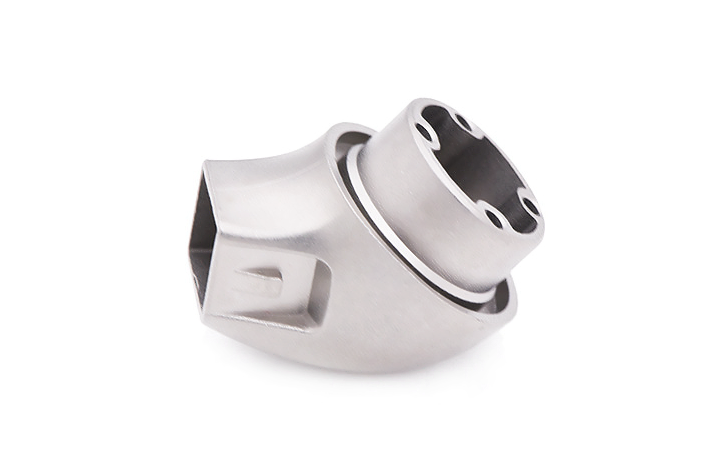
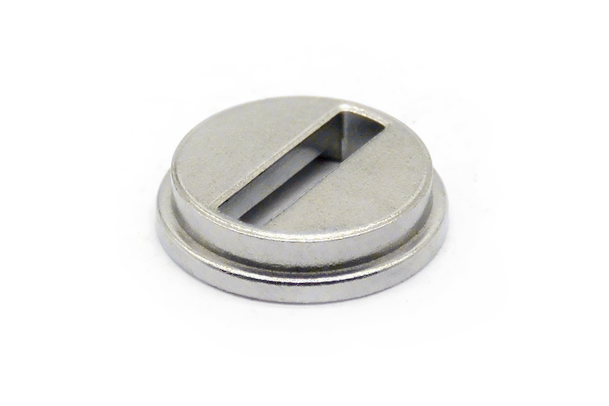
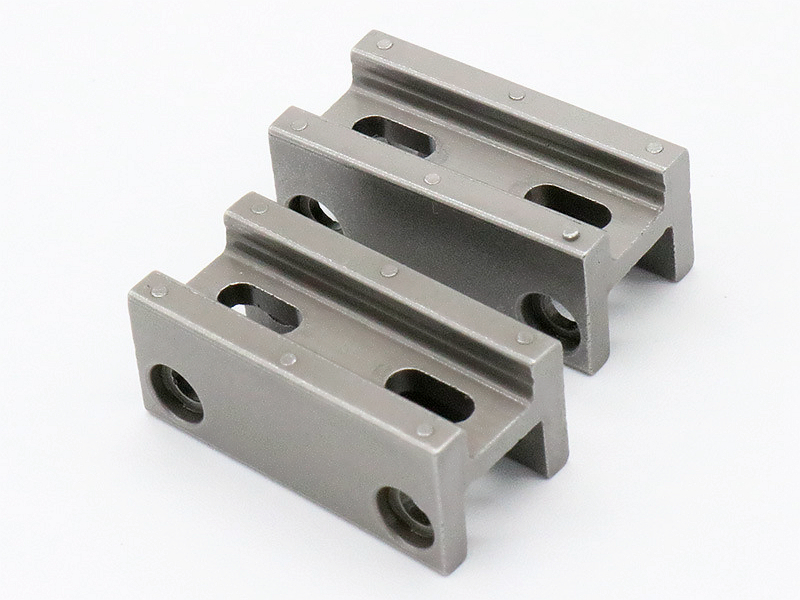
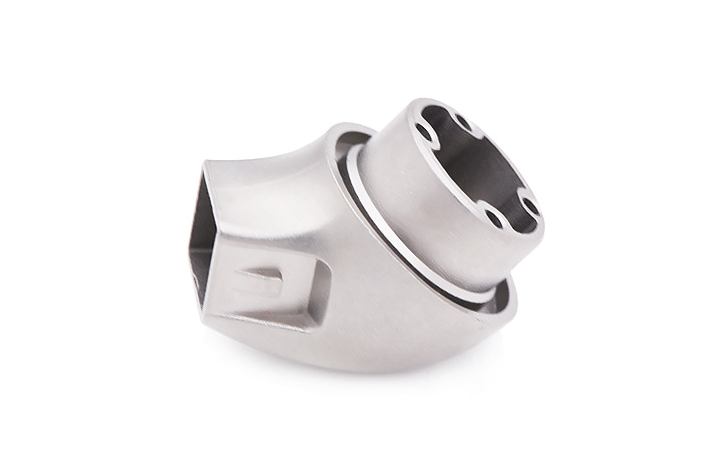
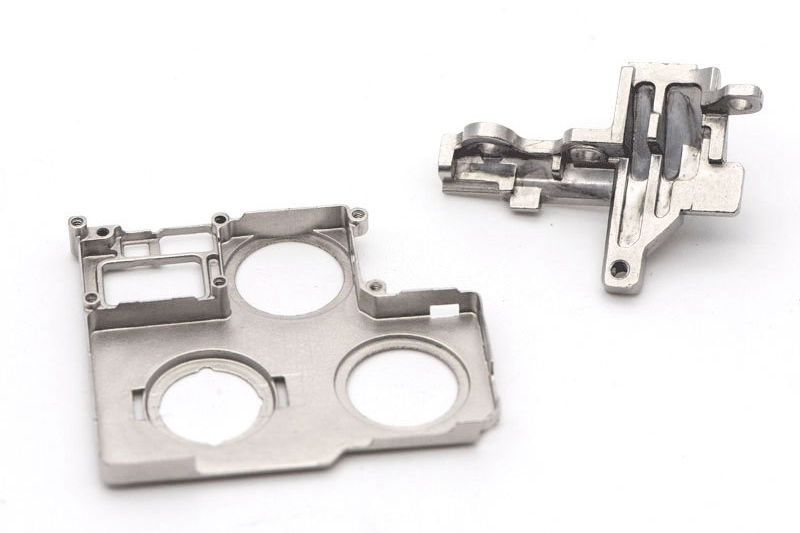
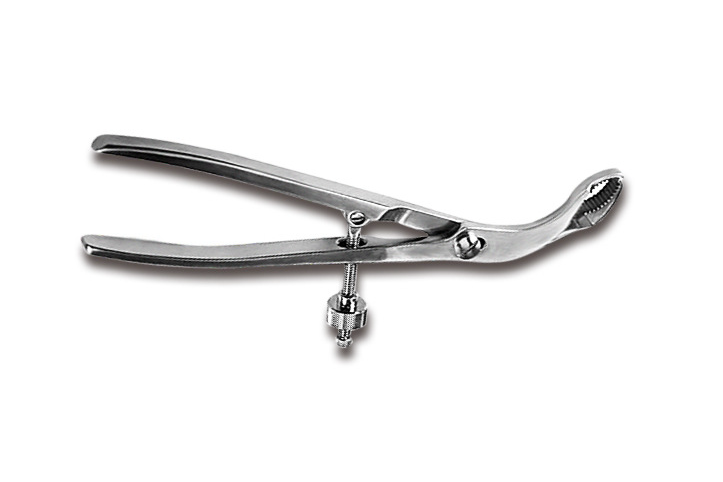
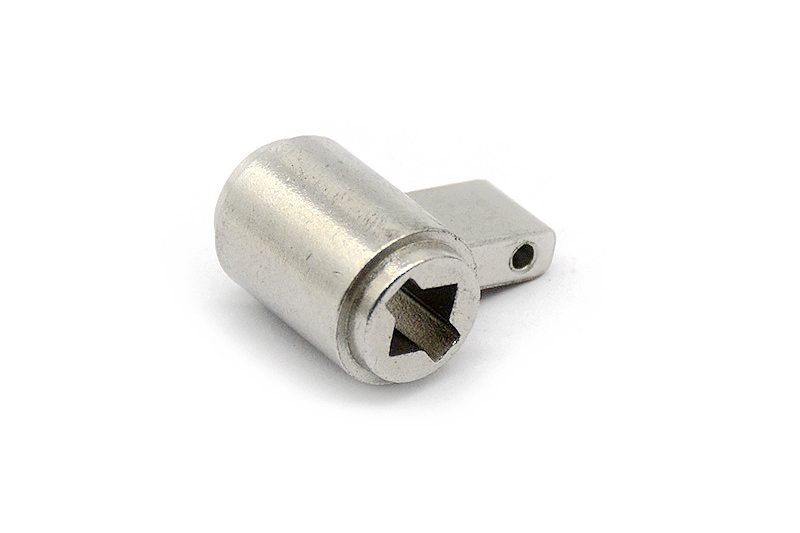
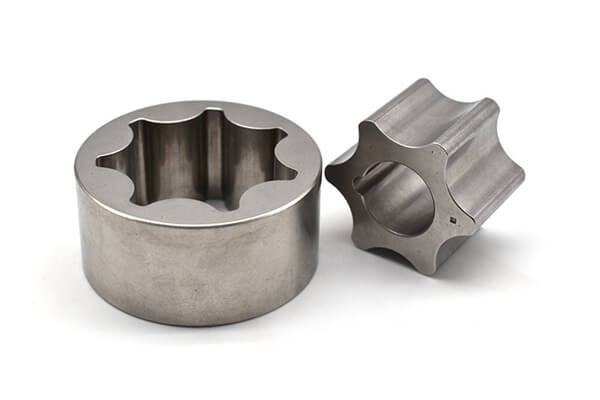
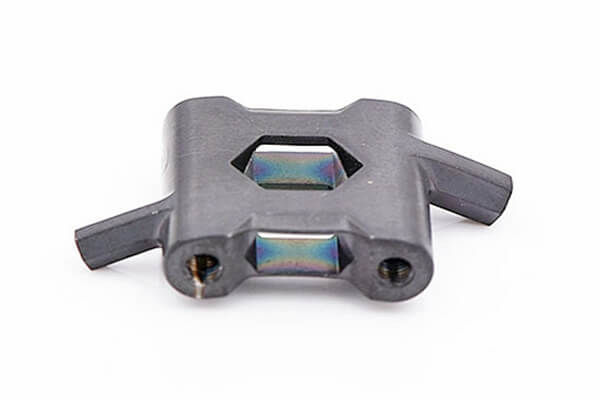
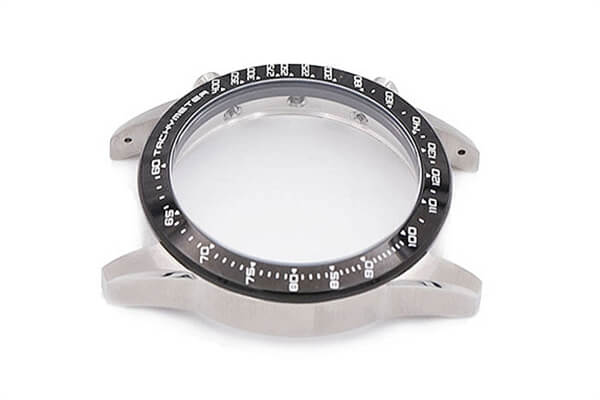
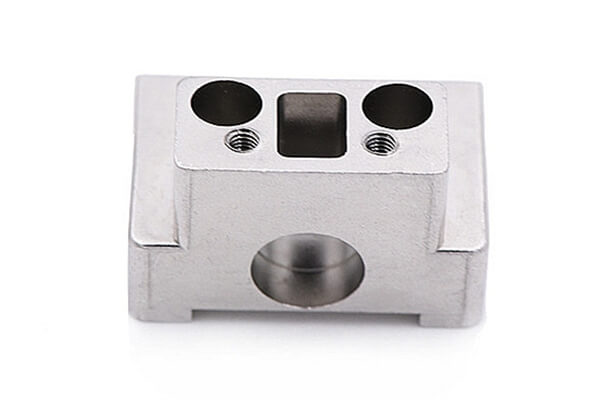
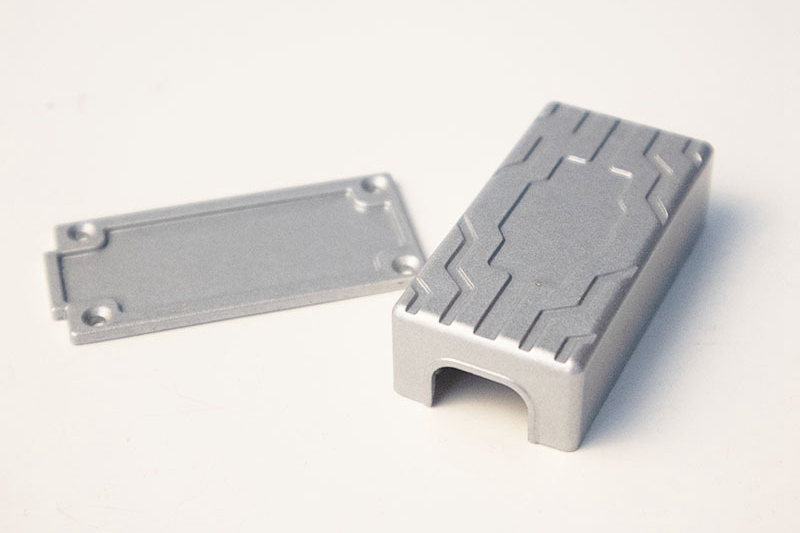
Small Complex Metal Parts Metal Injection Molding
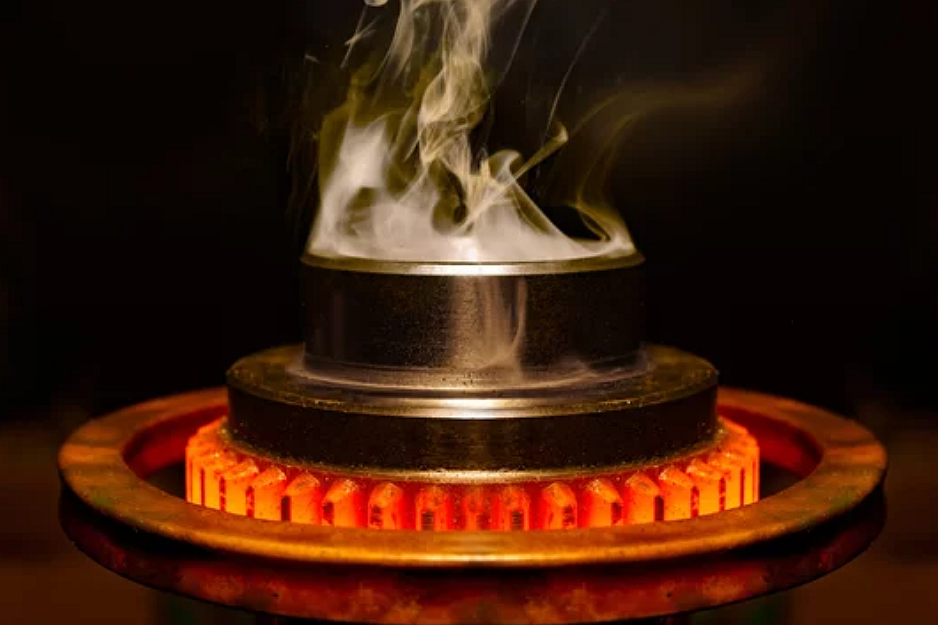
Metal injection molding combines powdered metal with a binder, injects it into molds, then heats it to remove the binder and sinter it into a durable part. Suitable for small, complex, high-precision metal parts manufacturing. The material selection range is wide, such as iron-based, nickel alloy, tungsten alloy, titanium alloy, superalloy alloy, etc.

Start Your MIM Parts Quote
All uploaded files are secure and confidential
What Is Metal Injection Molding Service
Our metal injection molding Service specializes in transforming metal powders into complex parts and components. We offer multi metal powder injection molding molding process. Such as iron base, tungsten, titanium, magnetic, and cobalt alloys injection molding. We produce high precision and strong custom MIM parts.
MIM Vs. PCM
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) and Powder Compression Molding (PCM) are distinct manufacturing processes. MIM uses fine metal powders for high-precision, complex parts, while PCM compresses powder into simpler shapes with lower precision. MIM is costlier and suited for medium to high volume production, whereas PCM is more economical for lower volumes.
Metal Injected Parts Applications
Our metal injection molding process produces high-quality parts with intricate details and superior strength. These metal injected parts find extensive use across various industries, offering precision and versatility for critical applications.
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) Materials
View How Metal Injection Molding Works
Metal injection molding is a net shape process that combines the advantages of plastic injection molding and powder metallurgy to produce highly complex metal parts and heavy alloy parts, such as stainless steel, titanium alloy, tungsten alloy, etc.
Custom Parts Surface Finishing Available
Our Surface Treatment Service offers specialized finishes for custom parts, enhancing durability, aesthetics, and performance. We provide a range of processes, including Electroplating, Anodizing, Powder Coating, and Thermal Barrier Coatings, tailored to improve corrosion resistance, wear properties, and visual appeal of metal and plastic components across industries.
learn more
As Machined
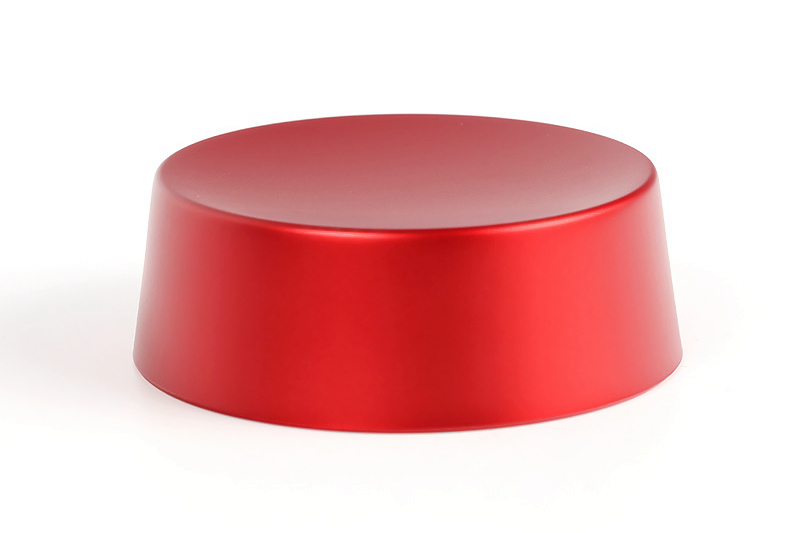

learn more
Painting

learn more
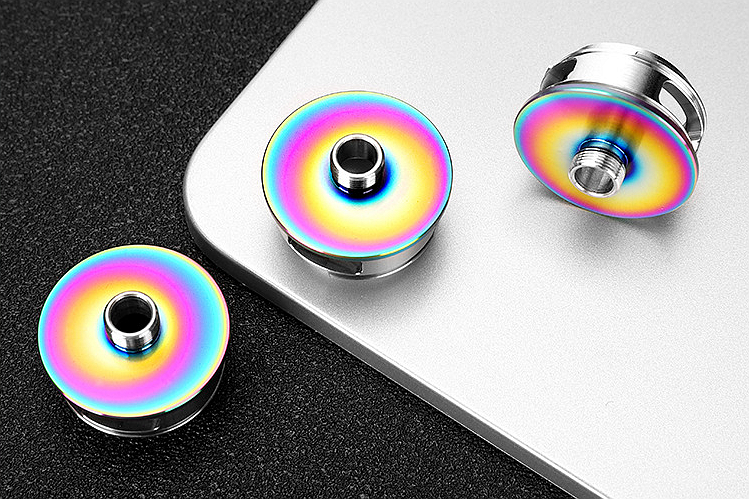
PVD

learn more
Sandblasting

learn more
Electroplating

learn more
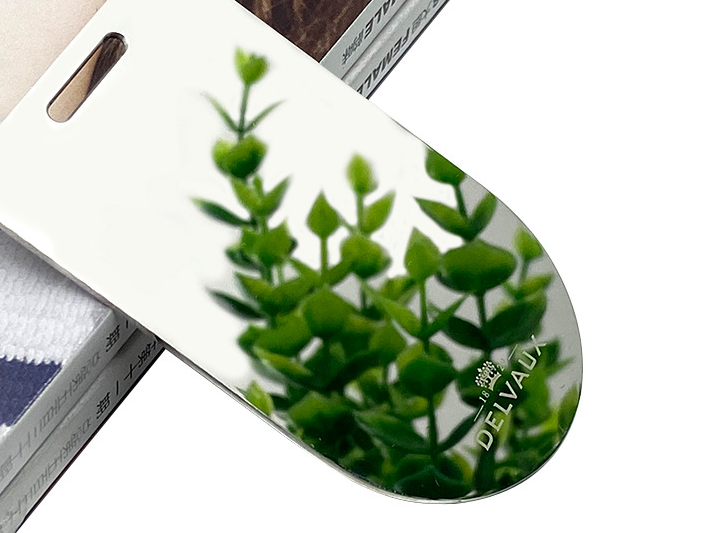
Polishing

learn more
Anodizing

learn more
Powder Coating

learn more
Electropolishing

learn more
IMD

learn more
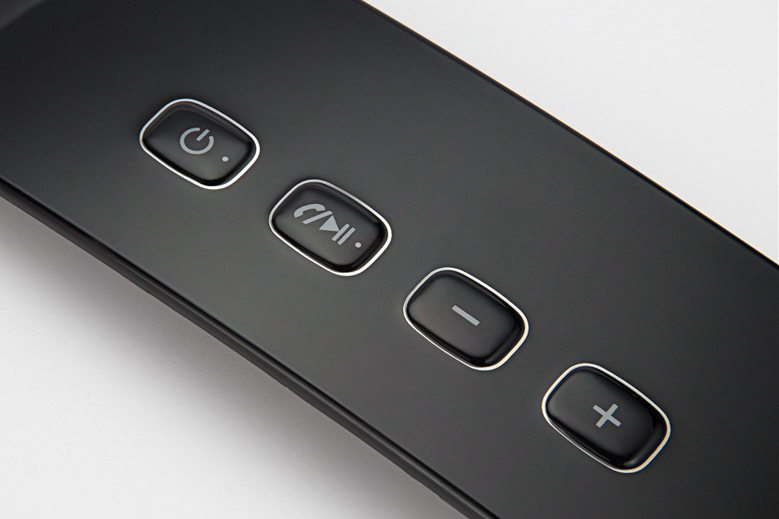
Brushed Finishes

learn more
Black Oxide
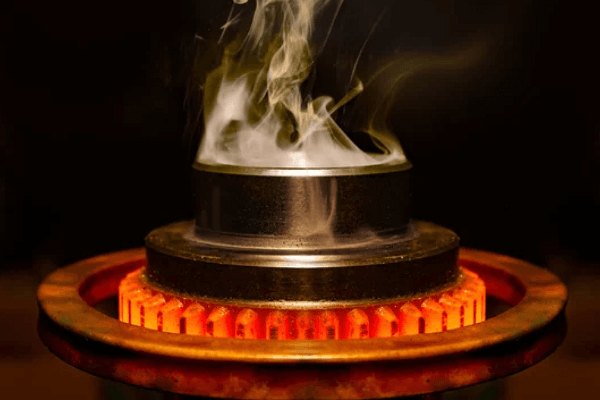

learn more
Heat Treatment
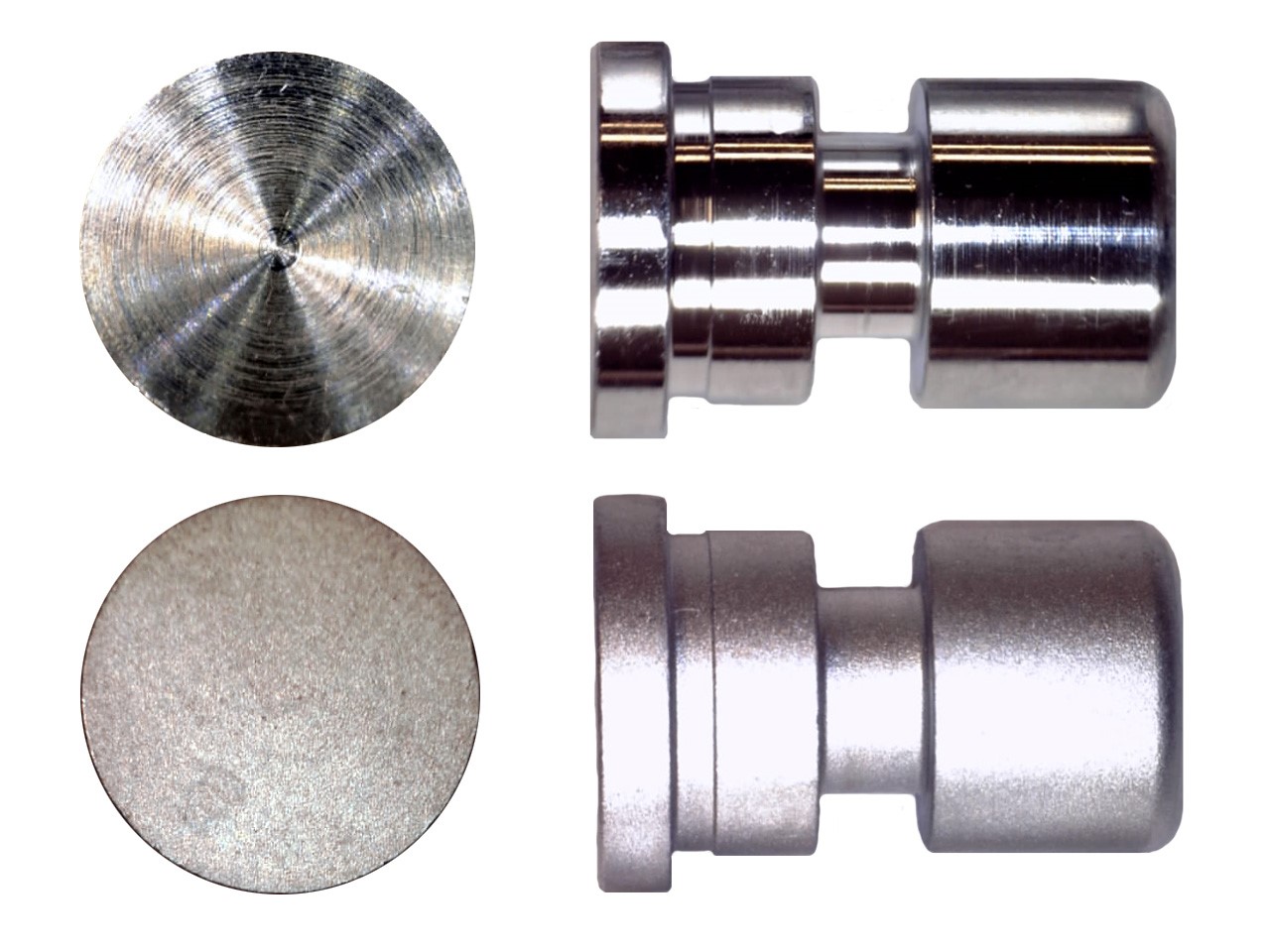

learn more
Tumbling
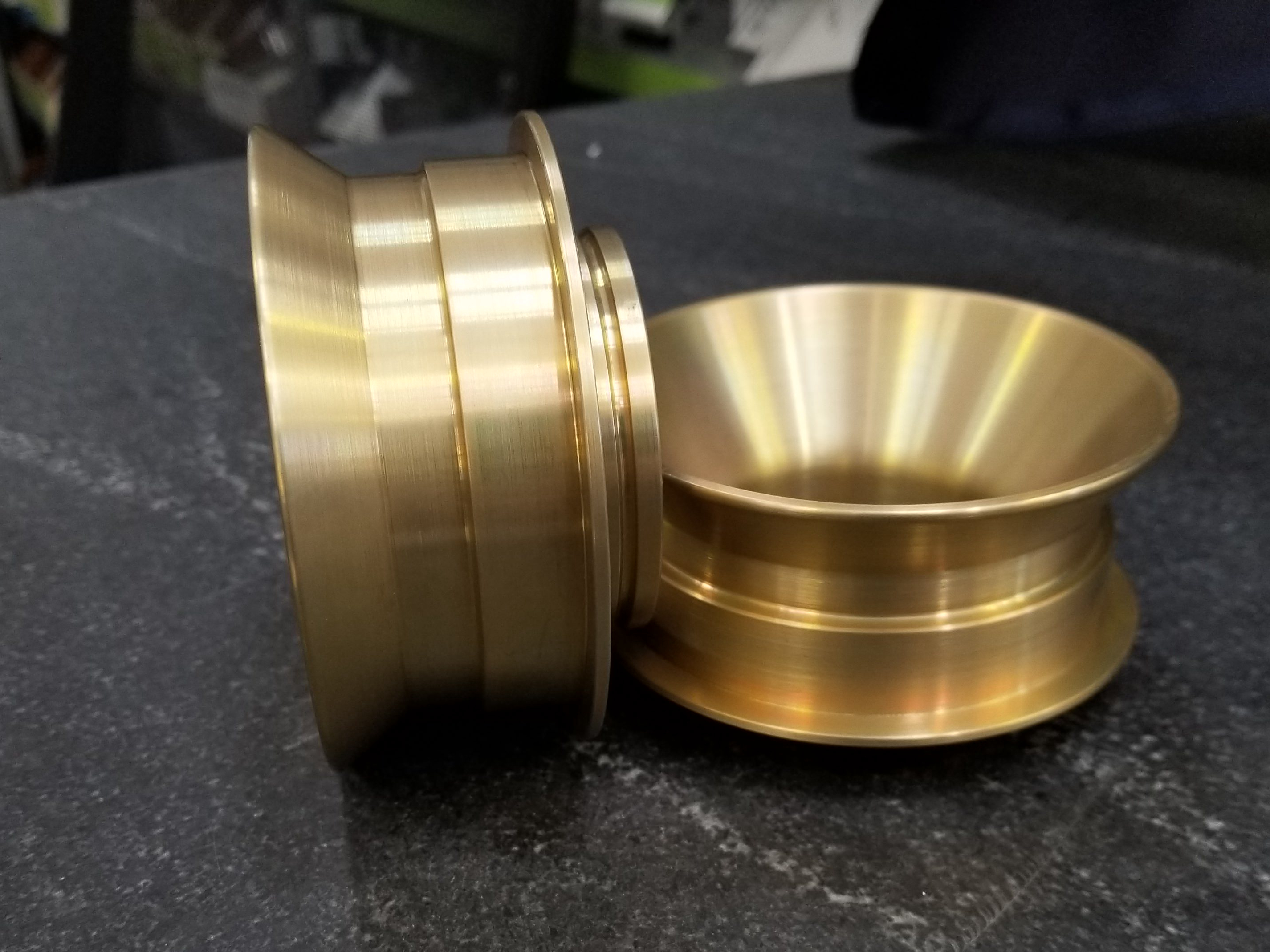

learn more
Alodine
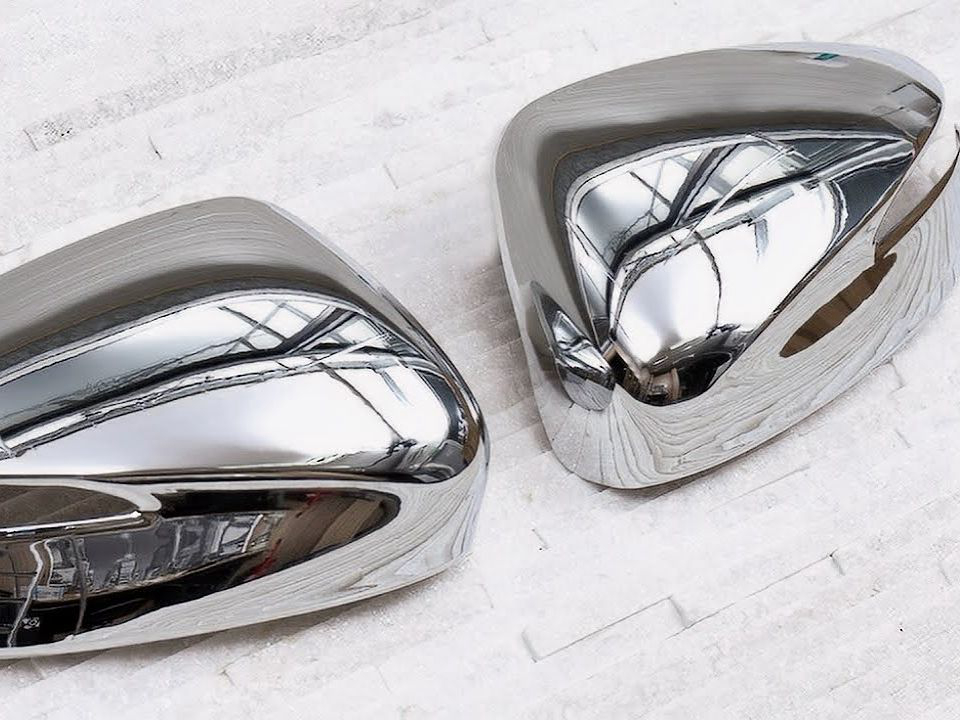

learn more
Chrome Plating
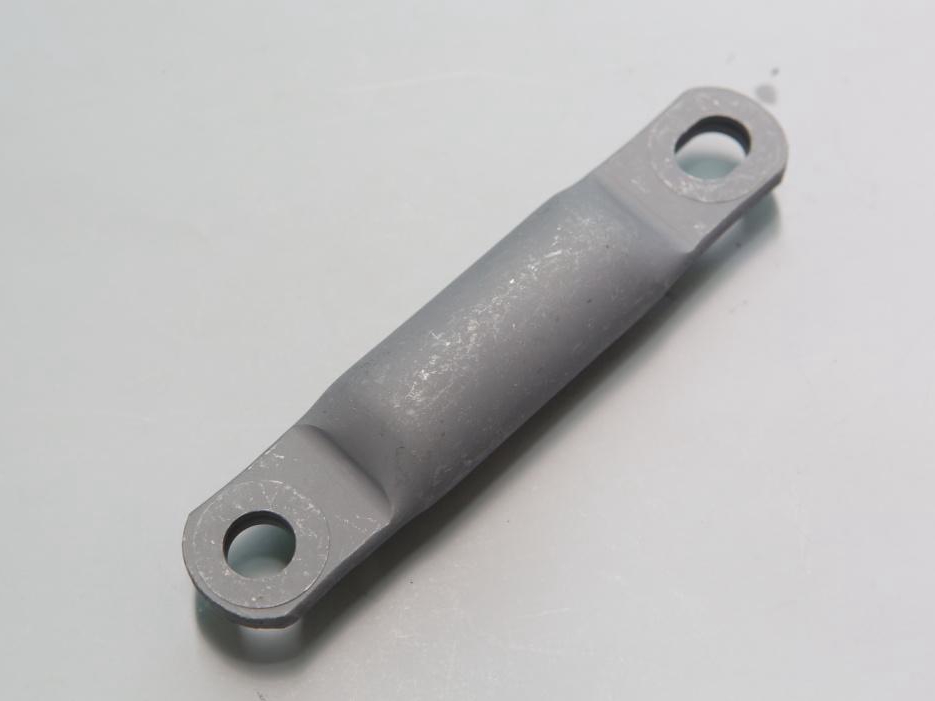

learn more
Phosphating

learn more
Nitriding

learn more
Galvanizing

learn more
Lacquer Coating

learn more
Teflon Coating
learn more
Thermal Coatings
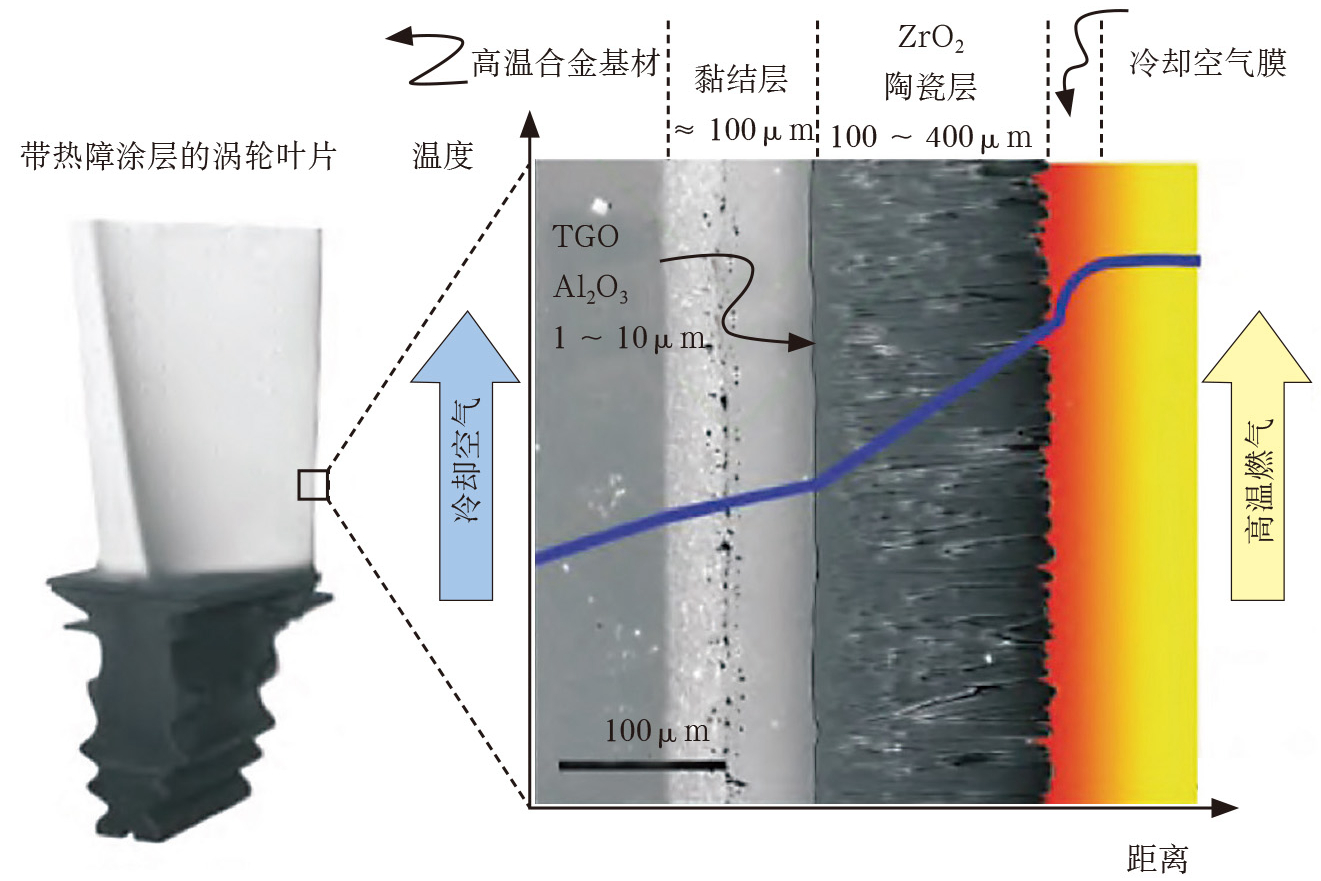
learn more
Thermal Barrier Coatings

learn more
Passivation
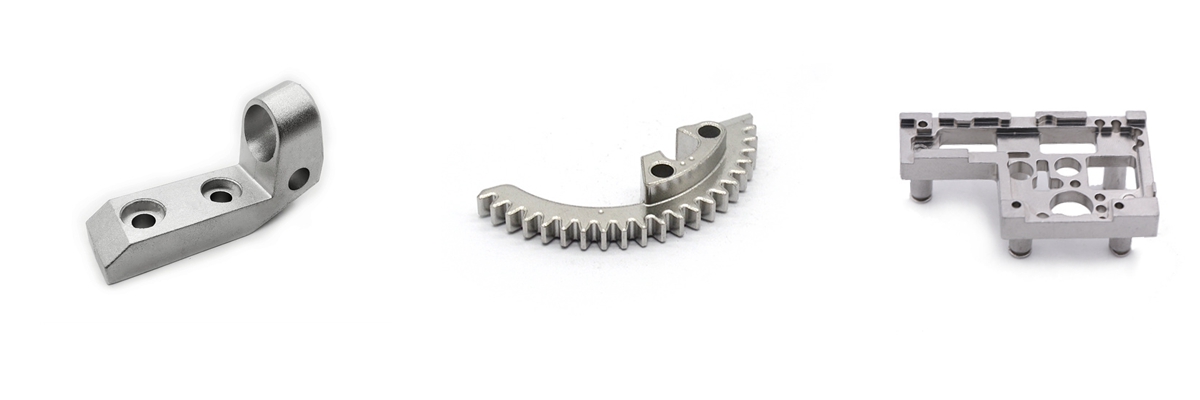
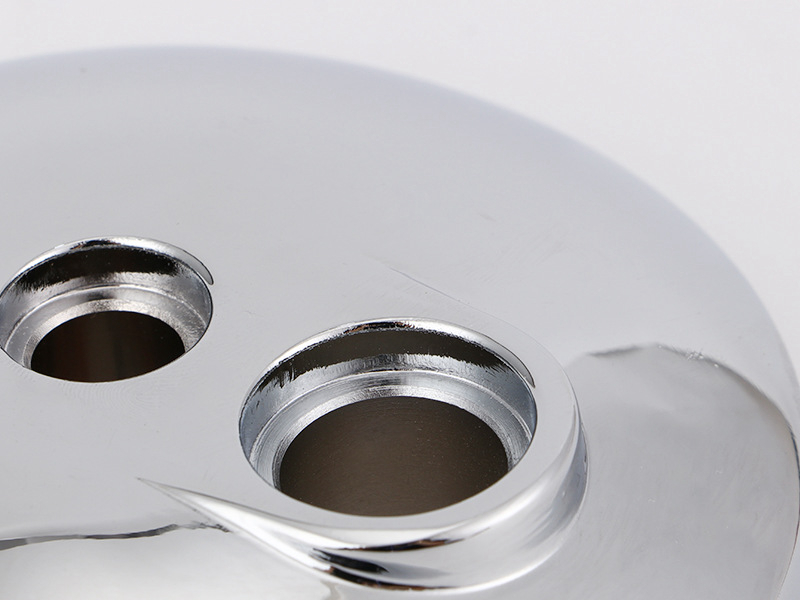
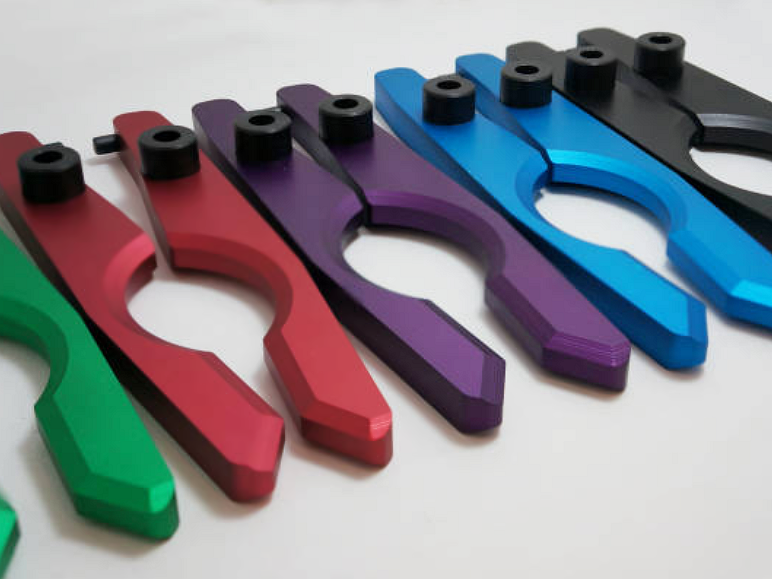
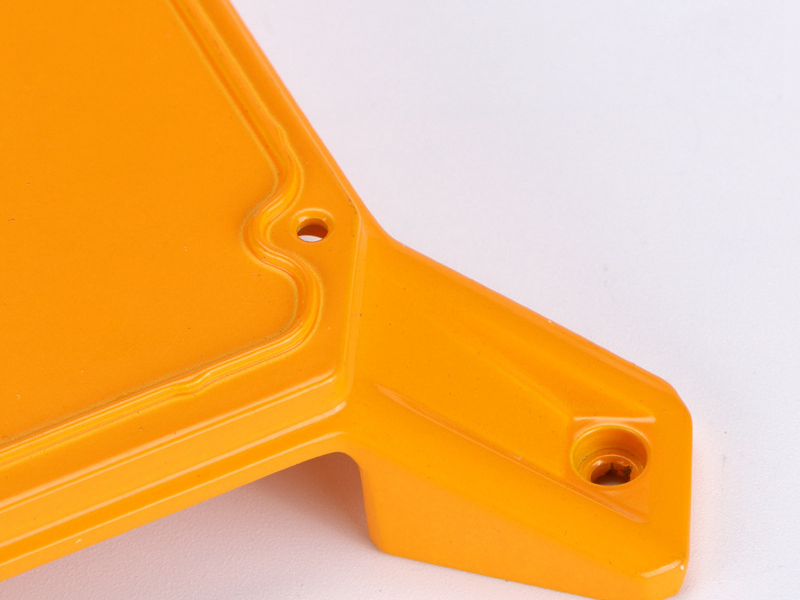
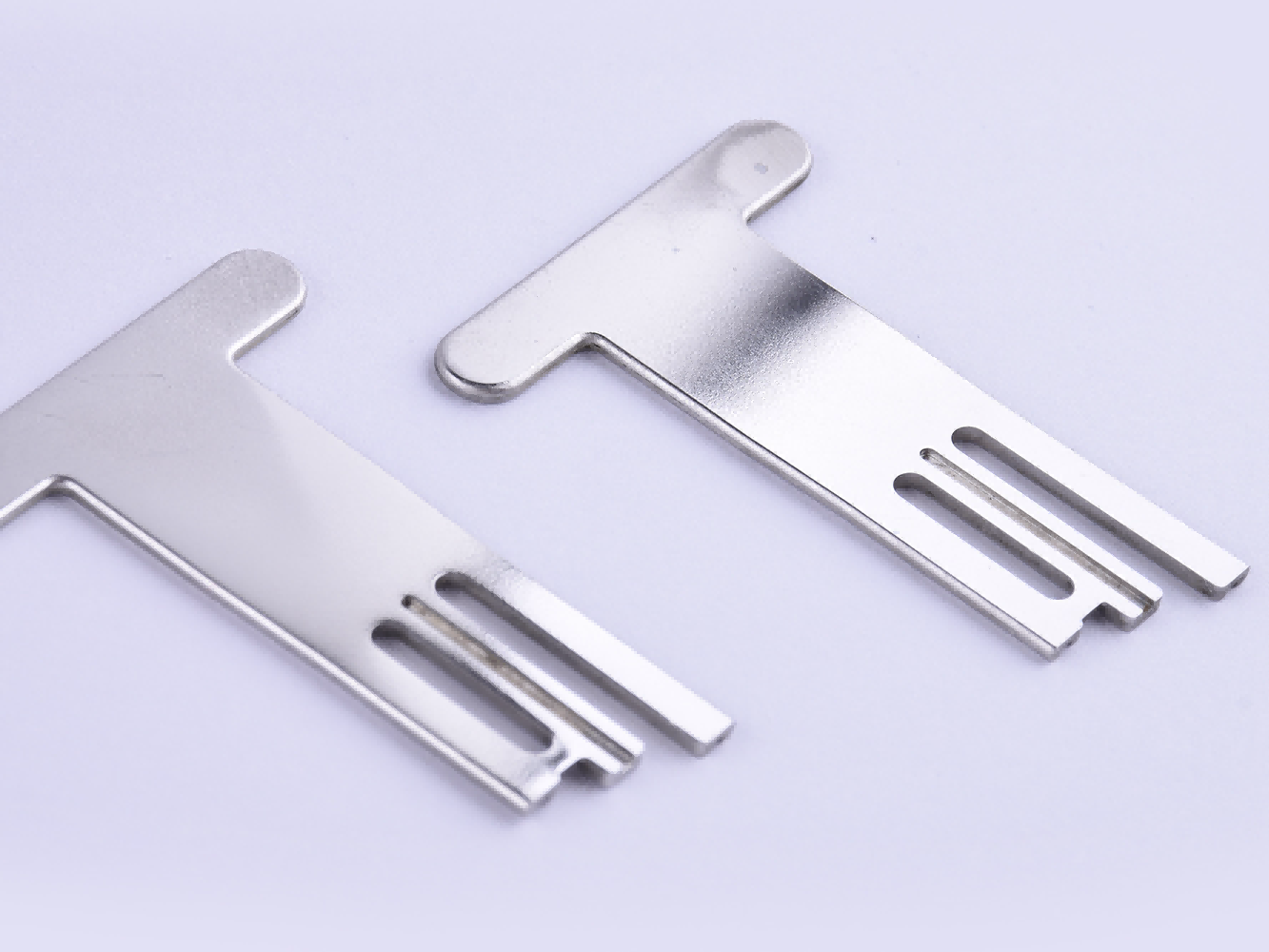
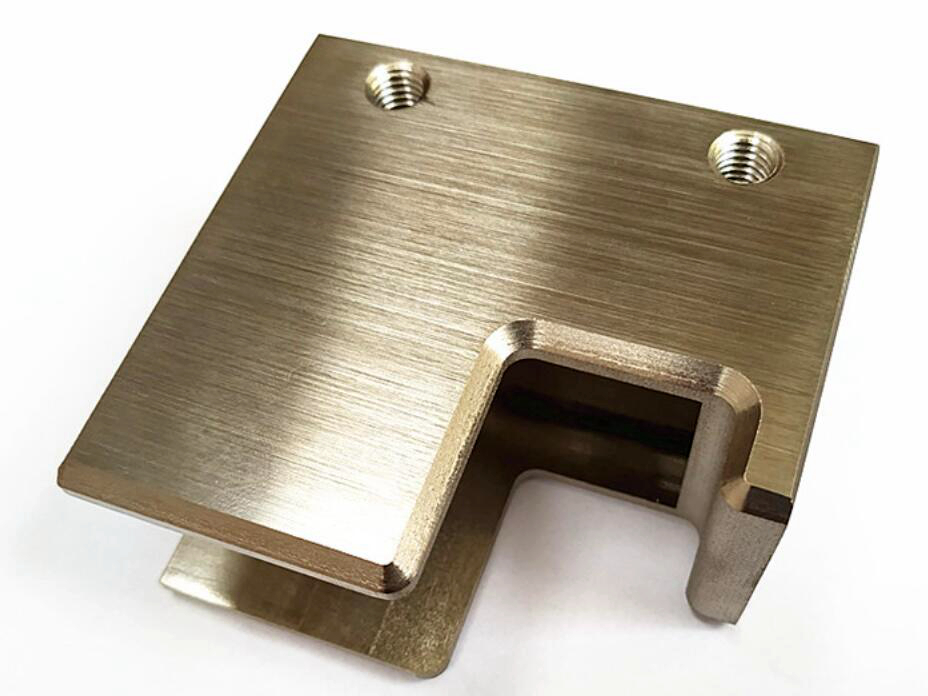
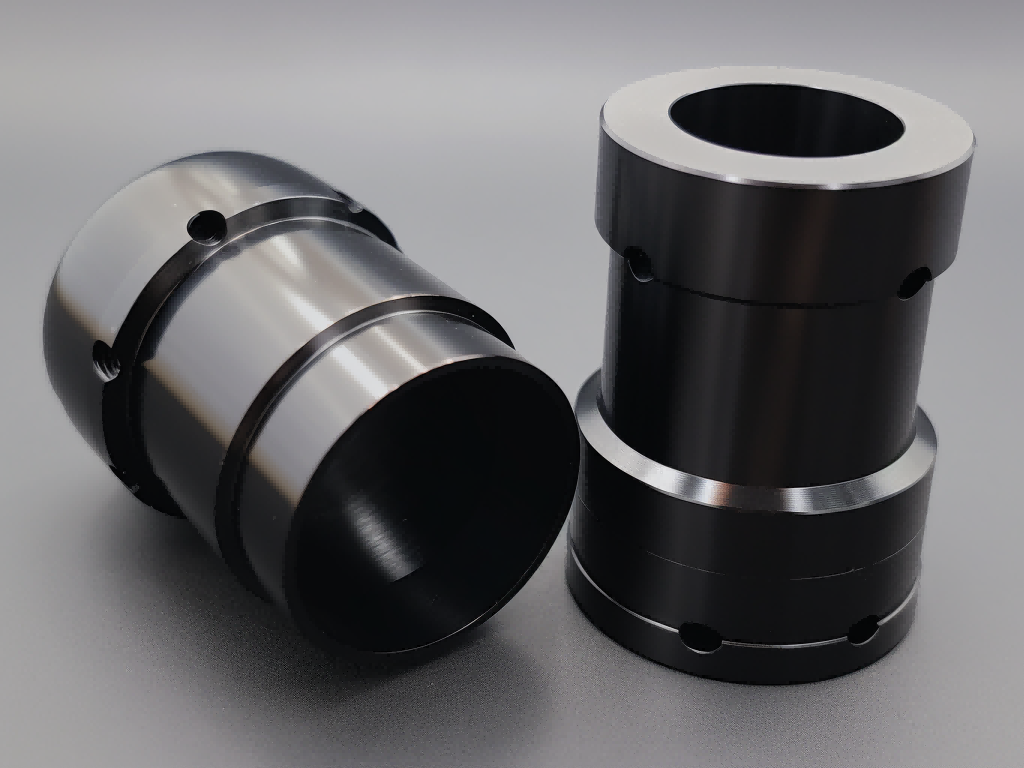
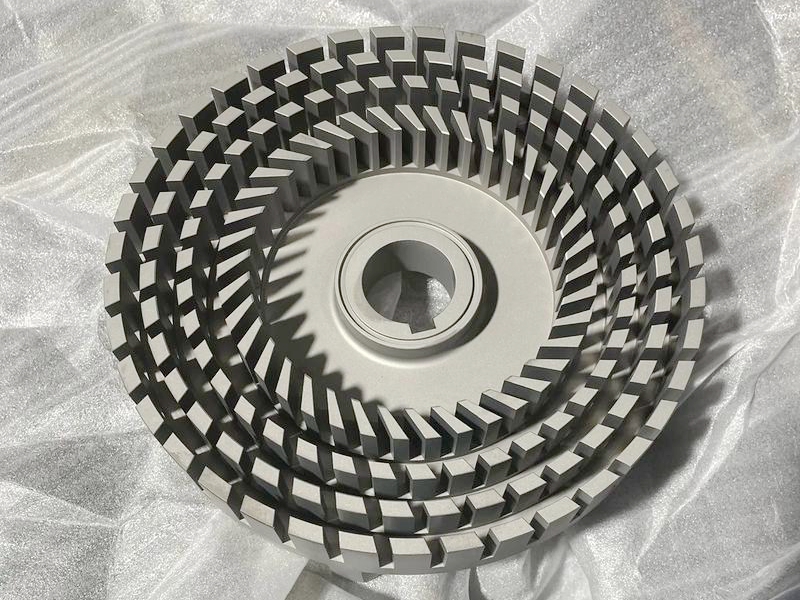
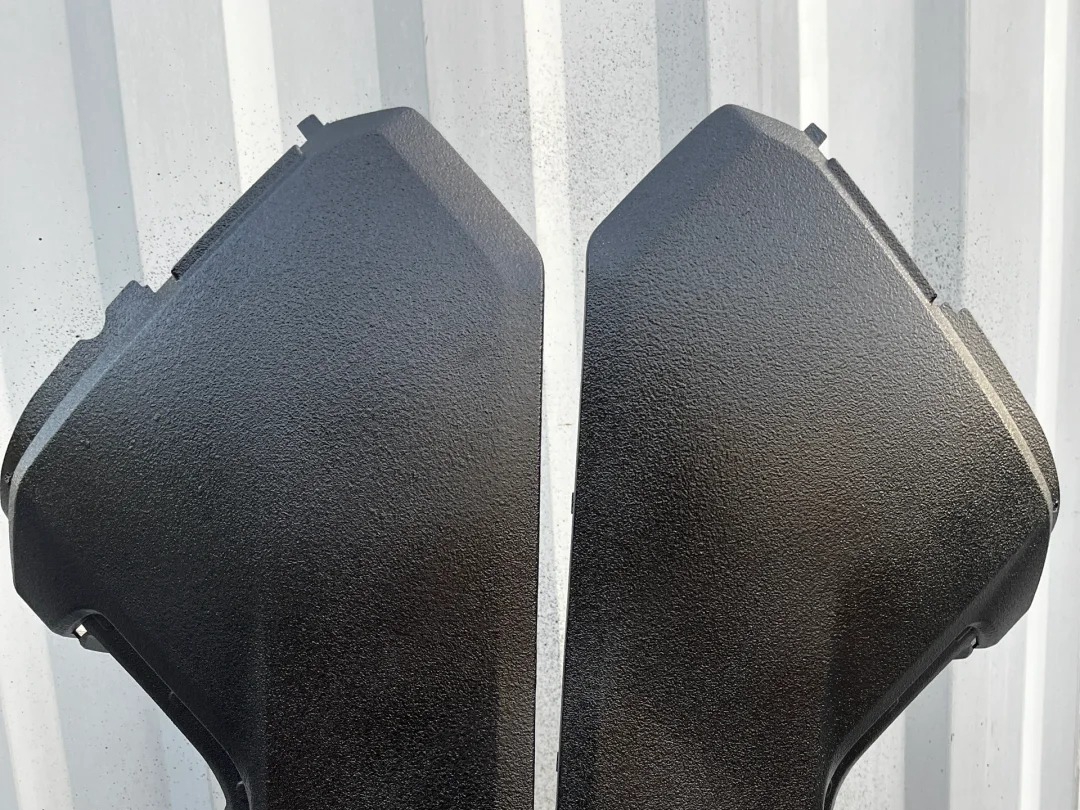
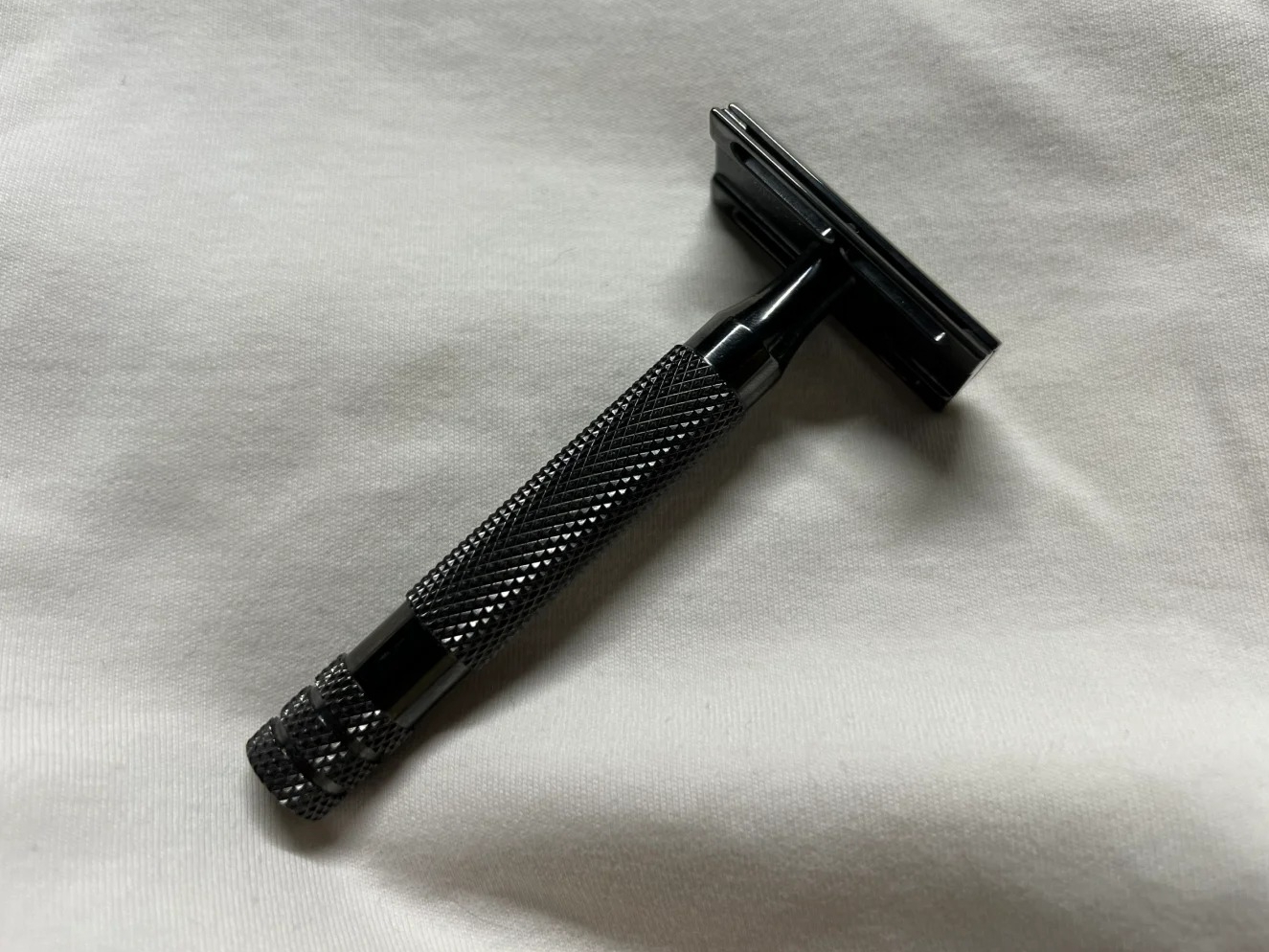
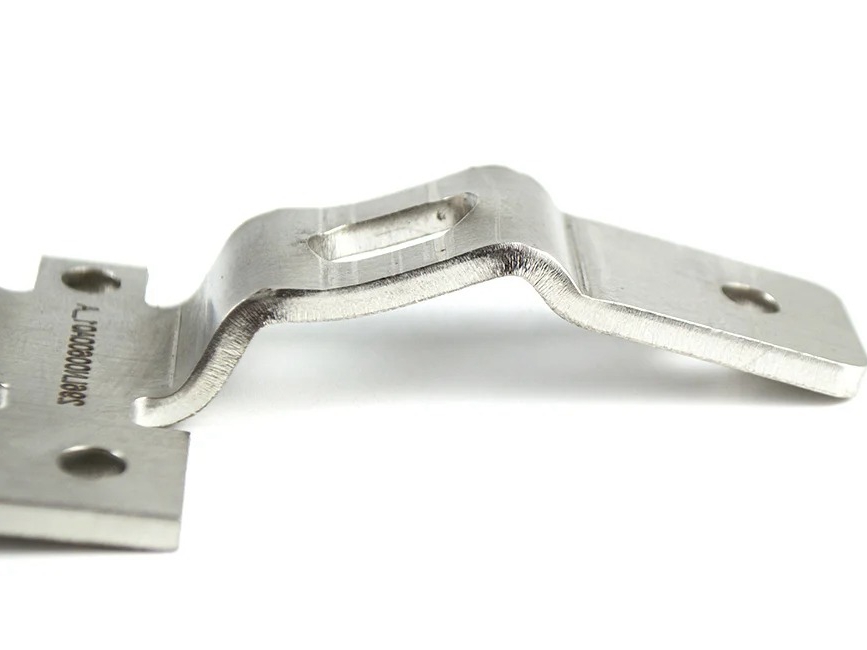
MIM Parts Gallery
At our MIM parts gallery, we understand that every project is unique. That's why we work closely with our customers to ensure that their custom parts are designed to meet their exact specifications. With our attention to detail and commitment to quality, you can trust that your custom parts will exceed your expectations.
Let's Start A New Project Today
MIM Parts Design Suggestion
Better understand the process limits of metal injection molding, such as limit size, tolerance, wall thickness, most efficient customization quantity, etc. Provide reference and save costs for your MIM part design.
Frequently Asked Questions
Explore Related Resources
Solutions
Copyright © 2025 Neway Precision Works Ltd.All Rights Reserved.