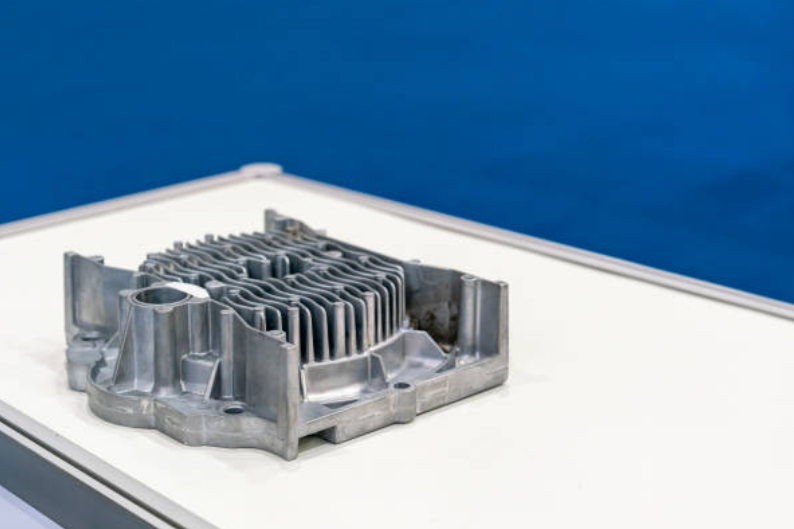
What Is Parting Line In Aluminum Die Casting Manufacturing?
In aluminum die-casting manufacturing, the parting line is a critical aspect of mold design, representing the interface where the two halves of the die meet. Understanding the parting line's role and management is crucial for ensuring the quality and integrity of the cast parts.
Definition and Importance
The parting line can be defined as the boundary line on a die casting where the two halves of the die or mold come together. During the casting process, molten aluminum is injected into the mold, which is split into two halves to allow for the opening and closing of the die and the removal of the finished part. The selection and placement of the parting line significantly affect the casting's quality, appearance, and dimensional accuracy.
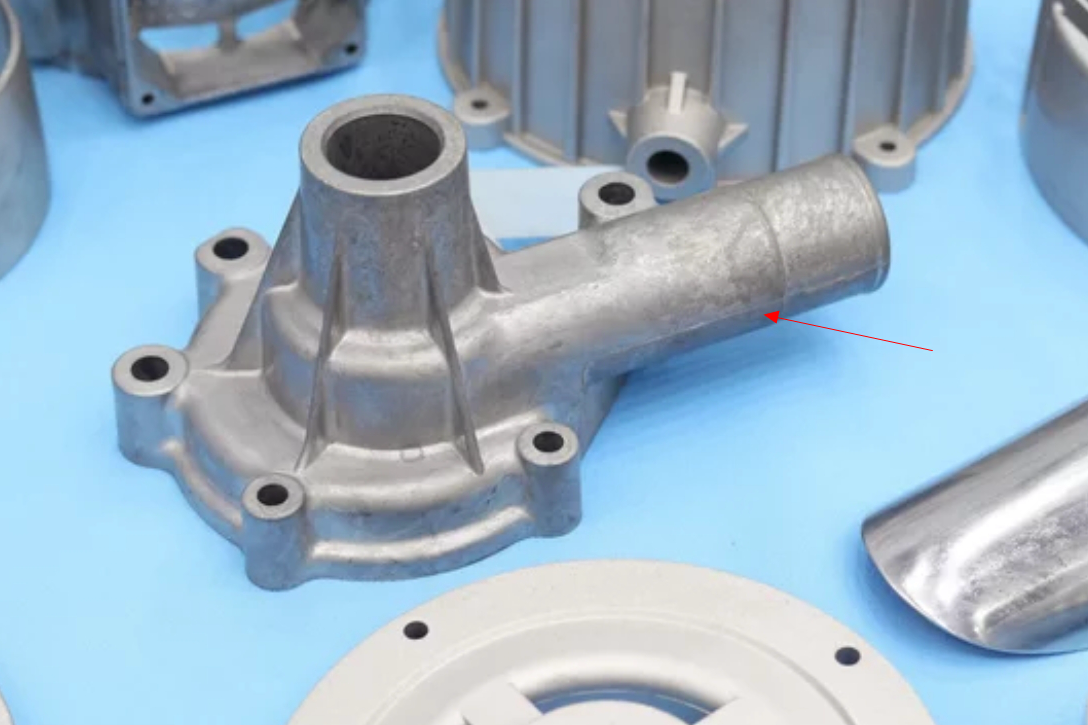

Functional Role
The parting line's placement determines several critical factors in both the design and production phases:
Mold Design and Complexity: Strategic parting line placement can reduce the complexity of the mold design, potentially lowering manufacturing costs and simplifying the casting process.
Quality of the Finished Product: A well-designed parting line minimizes the appearance of flash (excess material along the parting line) and other defects, such as misalignments or uneven surfaces. It ensures that these imperfections are placed in non-critical casting areas, where they can either be easily removed during finishing or will not affect the part's functionality.
Ease of Mold Fabrication and Maintenance: A simpler parting line can lead to fewer machining steps for mold creation and easier maintenance and cleaning of the mold, contributing to longer mold life and reduced downtime.
Aesthetic and Practical Considerations
Parting lines also play a significant role in the aesthetics of the final product, especially for consumer-facing parts where appearance is crucial. Designers aim to place parting lines in hidden or less noticeable areas to enhance the product's visual appeal. Additionally, the parting line's location can influence the casting's mechanical properties by affecting how the metal flows into the mold and solidifies.
Challenges
Managing parting lines involves addressing several challenges:
Placement Strategy: Determining the optimal placement of the parting line involves a balance between aesthetic considerations, functionality, and manufacturability.
Minimizing Flash and Other Defects: Improper parting line placement can lead to increased flash occurrences, affecting the part's quality and requiring additional post-processing work.
Mold Wear and Tear: The parting line is a common site for wear on the mold due to the constant opening and closing during the casting cycle, which can affect the longevity and performance of the mold.
In summary, the parting line in aluminum die casting is a fundamental aspect of mold design that significantly impacts the manufacturing process's efficiency, the quality of the finished parts, and the overall cost of production. Effective management of parting lines is crucial for optimizing the casting process and achieving the desired outcomes in terms of both functionality and aesthetics.