383 (ADC12)
What Is Cast Aluminum 383 (ADC12)
Cast Aluminum 383, also known as ADC12, is an aluminum alloy widely used in the die-casting process. It is a versatile material with favorable characteristics for various applications. ADC12 consists mainly of aluminum and smaller percentages of other elements, including silicon, copper, iron, and zinc.
The designation ADC12 follows the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) for aluminum die-casting alloys. The "A" in ADC12 indicates that it is an aluminum alloy, and "DC" stands for die-casting. "12" specifies the specific alloy composition within the ADC series.
ADC12 offers excellent castability, high corrosion resistance, and good mechanical properties. It is commonly used in automotive components, electrical housings, and other applications requiring lightweight and durable metal parts. The silicon content in ADC12 enhances fluidity during the casting process, contributing to intricate and precise mold filling.
In summary, Cast Aluminum 383 (ADC12) is a well-suited alloy for die casting. Its balanced properties make it famous for producing high-quality, intricate aluminum components in various industries.
Key Features And Applications of Aluminum 383 (ADC12) Castings
Aluminum 383, also known as ADC12, is a widely used aluminum alloy in casting due to its favorable properties. Here are key features and applications:
Key Features:
High Fluidity: ADC12 has excellent fluidity during casting, allowing intricate and detailed molds to be filled effectively.
Good Machinability: This alloy is known for its machinability, making it easier to work with in post-casting processes such as machining and finishing.
Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum 383 exhibits good resistance to corrosion, enhancing its durability and suitability for various applications, even in challenging environments.
High Strength: It possesses a good balance of strength and lightweight characteristics, making it suitable for applications where strength and reduced weight are essential.
Heat Resistance: ADC12 maintains its mechanical properties at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for applications where exposure to heat is a consideration.
Applications:
Automotive Components: ADC12 is commonly used in the automotive industry for casting components such as engine parts, transmission cases, and structural components due to its strength, lightweight nature, and thermal resistance.
Consumer Electronics: The alloy is utilized in the casting of various components in consumer electronics, including housings for electronic devices, heat sinks, and connectors.
Industrial Components: ADC12 finds applications in producing various industrial components, such as pump housings, valve bodies, and other parts where a combination of strength and corrosion resistance is crucial.
Building and Construction: Due to its corrosion resistance and versatility, it is employed in casting architectural and construction components like brackets, fittings, and decorative elements.
General Engineering: ADC12 is used in various general engineering applications where a balance of strength, durability, and formability is required.
In summary, Aluminum 383 (ADC12) is a versatile alloy with properties that make it well-suited for various casting applications, particularly in automotive, electronics, construction, and general engineering industries.
Properties of Aluminum 383 (ADC12) Alloys
Chemical Comparison of Aluminum 383 (ADC12)
Element | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Ni | Zn | Sn | Pb | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Composition (%) | 9.6-12.0 | 1.3 | 1.5-3.5 | 0.5 | 0.3-0.6 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.2 | Balance |
Function of Chemical Components
Indeed, the chemical components in Aluminum 383 (ADC12) play crucial roles in determining its properties and performance.
Silicon (Si):
Function: Silicon contributes to the alloy's strength and fluidity during casting. It forms a solid solution with aluminum, enhancing the overall mechanical properties.
Iron (Fe):
Function: Iron is a common impurity but is generally kept low in aluminum alloys. It can impact the alloy's mechanical properties, and controlling its content is essential for maintaining the desired characteristics.
Copper (Cu):
Function: Copper improves the alloy's strength and corrosion resistance. However, excessive copper content can lead to hot cracking during casting, so the level is carefully controlled.
Manganese (Mn):
Function: Manganese enhances the castability of the alloy and contributes to its strength. It also acts as a deoxidizer, helping to remove undesirable oxygen from the melt.
Magnesium (Mg):
Function: Magnesium provides strength and heat resistance to the alloy. It plays a crucial role in forming the primary phase, contributing to the alloy's overall performance.
Nickel (Ni):
Function: Nickel is often added to improve the alloy's strength and toughness. It also contributes to the alloy's resistance to corrosion and oxidation.
Zinc (Zn):
Function: Zinc enhances the alloy's casting characteristics and provides additional strength. However, excessive zinc can lead to reduced corrosion resistance.
Aluminum (Al):
Function: Aluminum is the primary component and serves as the base metal. It provides the alloy with its inherent lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties.
In summary, each chemical component in Aluminum 383 (ADC12) contributes to specific aspects of the alloy's performance, including strength, castability, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance. Precisely controlling these components is essential to achieving the desired material properties for various applications.
Physical and Mechanical Properties
Tensile Strength (MPa) | Yield Strength (MPa) | Hardness (Brinell) | Shear Strength (MPa) | Impact Strength (J) | Fatigue Strength (MPa) | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Density (g/cm³) | Melting Range (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
305 | 230 | 82 | 185 | 8.5 | 70 | 96.2 | 2.68 | 570-640 |
Typical Applications of Aluminum 383 (ADC12) Castings
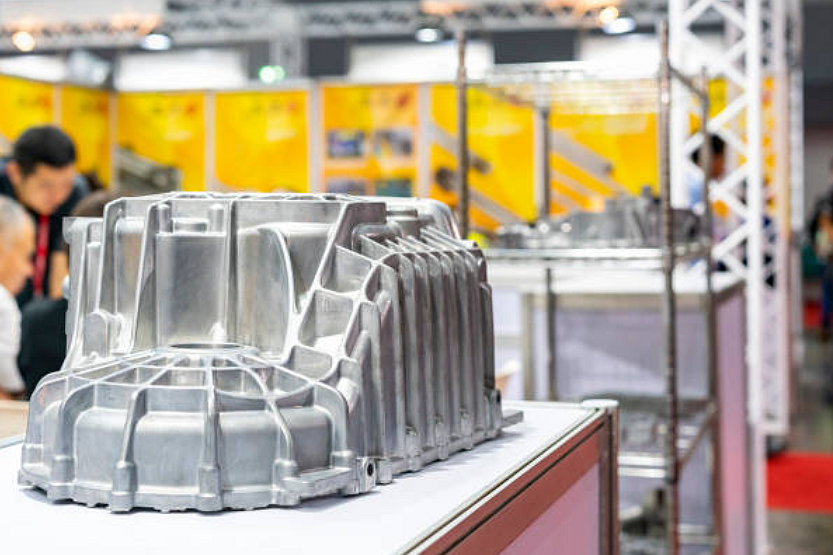
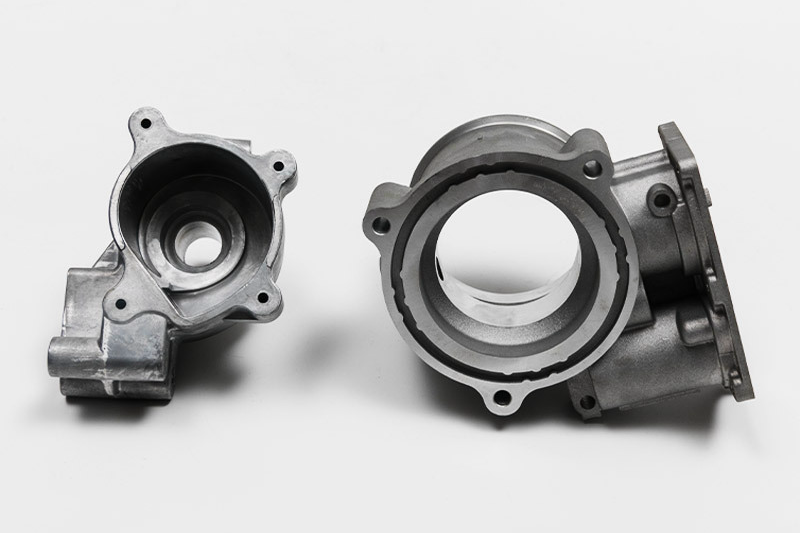
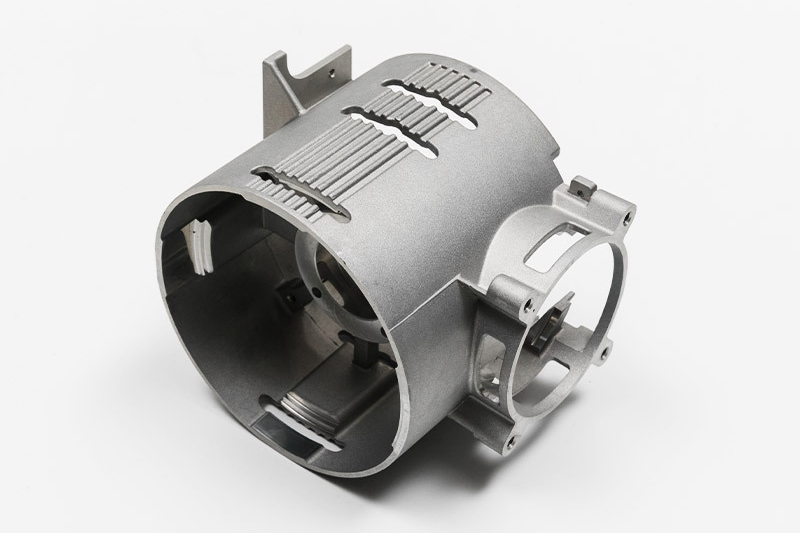
Aluminum 383 (ADC12) cast Automotive Components
Aluminum 383 (ADC12) is a favored material for casting automotive components due to its exceptional mechanical properties, lightweight nature, and corrosion resistance. One key advantage is its high tensile strength of 305 MPa, providing the structural integrity required for automotive applications. This strength, coupled with a yield strength of 230 MPa, ensures that the cast components can withstand the dynamic stresses experienced in automotive environments, contributing to the overall safety and durability of the vehicles.
The lightweight characteristics of Aluminum 383 (ADC12) play a pivotal role in enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing the vehicle's overall weight. With a density of 2.68 g/cm³, significantly lower than many alternative materials, the alloy allows for the production of lightweight yet sturdy automotive components. It contributes to improved fuel economy and enhances the overall performance and handling of the vehicle.
Furthermore, the corrosion resistance of Aluminum 383 (ADC12) is a crucial factor in its suitability for automotive applications. The alloy's corrosion resistance ensures the cast components' longevity, even in challenging environmental conditions, making it well-suited for various automotive parts, including engine components, transmission cases, and structural elements. The corrosion-resistant properties contribute to the overall reliability and longevity of the vehicles in which these components are utilized. In conclusion, the mechanical strength, lightweight nature, and corrosion resistance of Aluminum 383 (ADC12) make it an ideal choice for casting automotive components, contributing to modern vehicles' efficiency, performance, and durability.
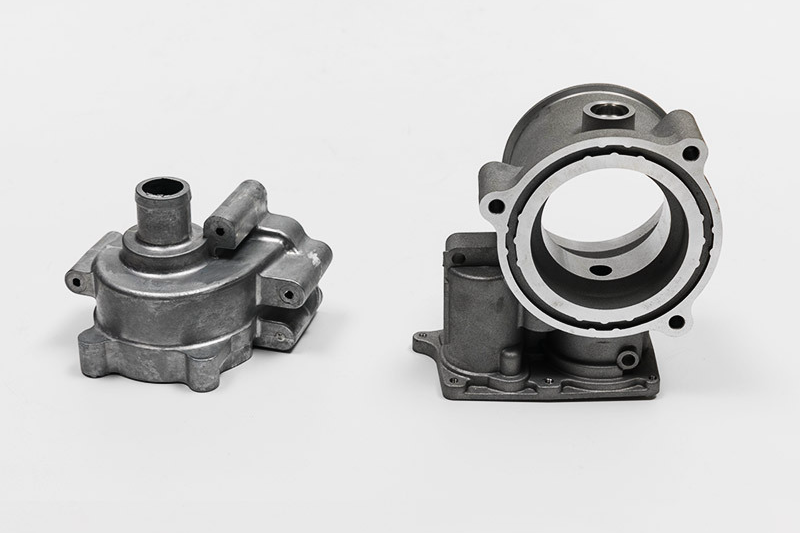


Aluminum 383 (ADC12) cast Consumer Electronics Housing
Due to its favorable properties, Aluminum 383 (ADC12) is preferred for casting consumer electronics housings. Its high fluidity during casting allows for intricate and complex mold designs commonly found in electronic device housings. The alloy's ability to fill detailed molds effectively ensures that the final castings exhibit the precise and intricate features necessary for modern consumer electronic products.
Secondly, ADC12 offers excellent machinability, allowing for post-casting processes such as machining and finishing. It is crucial in producing consumer electronics, where precise dimensions and smooth finishes are essential for aesthetic and functional purposes. The ease of machining also contributes to the cost-effectiveness of manufacturing electronic housings, making ADC12 a practical choice for mass production.
Lastly, the corrosion resistance of Aluminum 383 enhances the durability of consumer electronics housings. Electronic devices are often subjected to various environmental conditions, including exposure to moisture and temperature variations. The corrosion-resistant properties of ADC12 help protect the housing from degradation over time, ensuring the longevity and reliability of consumer electronics products. Overall, Aluminum 383 (ADC12) stands out as a versatile and reliable material for casting consumer electronics housings, meeting the stringent requirements of both form and function in the electronic manufacturing industry.
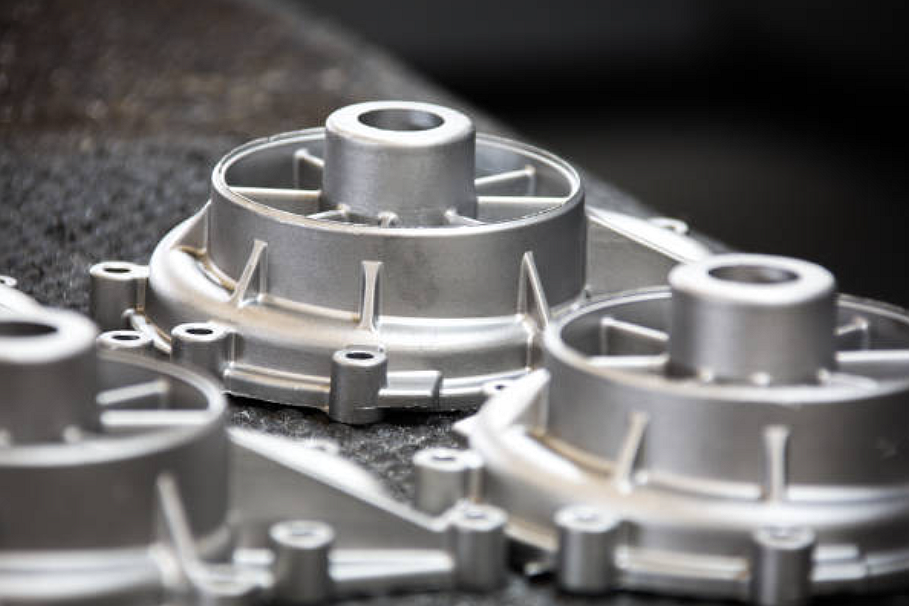
Aluminum 383 (ADC12) cast Industrial Components.
Aluminum 383 (ADC12) is well-suited for casting industrial components due to its unique combination of mechanical properties and casting characteristics. Its high fluidity during casting allows for complex industrial components' detailed and intricate molding. It ensures that the final products have precise shapes and dimensions, meeting the stringent requirements often demanded in industrial applications.
Secondly, the alloy's excellent machinability contributes to its versatility in industrial component manufacturing. Machining processes like milling and drilling are commonly employed in producing industrial parts. The good machinability of ADC12 simplifies these post-casting processes, allowing for the efficient fabrication of intricate components with tight tolerances.
Thirdly, the inherent properties of Aluminum 383, including its high strength, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance, make it a reliable choice for industrial applications. Industrial components often face challenging operating conditions, and ADC12's ability to maintain its mechanical integrity at elevated temperatures and resist corrosion ensures the longevity and durability of the cast components in diverse industrial environments. In summary, Aluminum 383's combination of casting characteristics, machinability, and robust mechanical properties positions it as a favorable material for casting various industrial components.

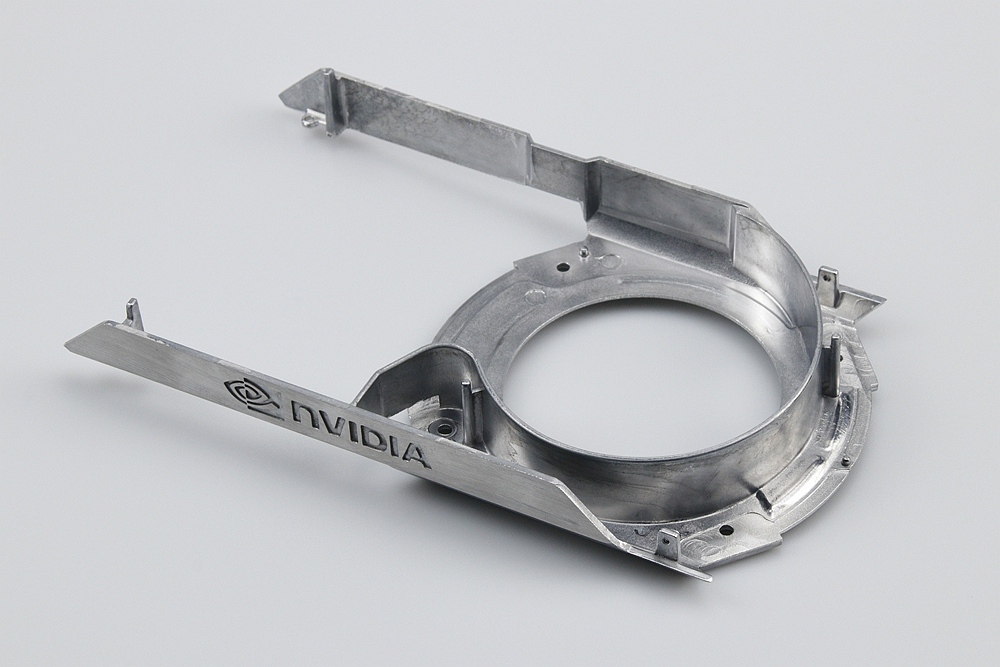
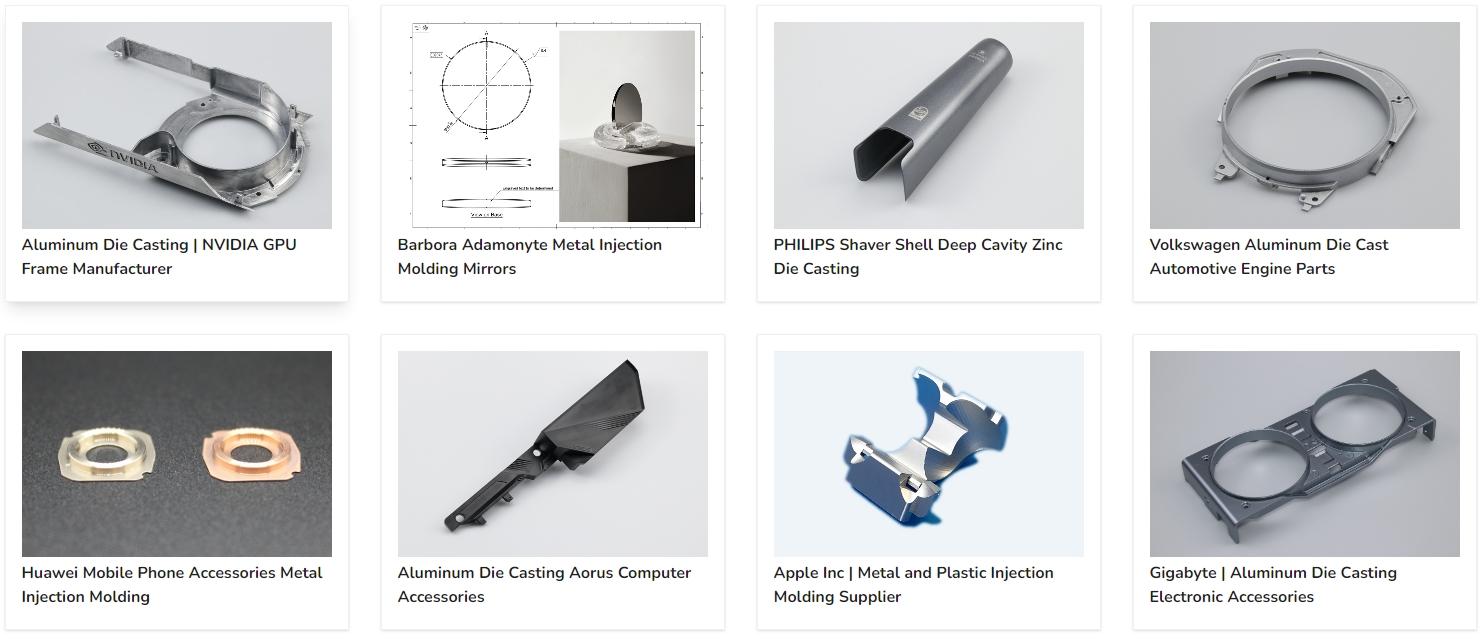
Brand Case Study
Neway has served many world-renowned companies, using its strong manufacturing capabilities and complete quality control system to provide further market competitiveness and quality assurance for major brands.