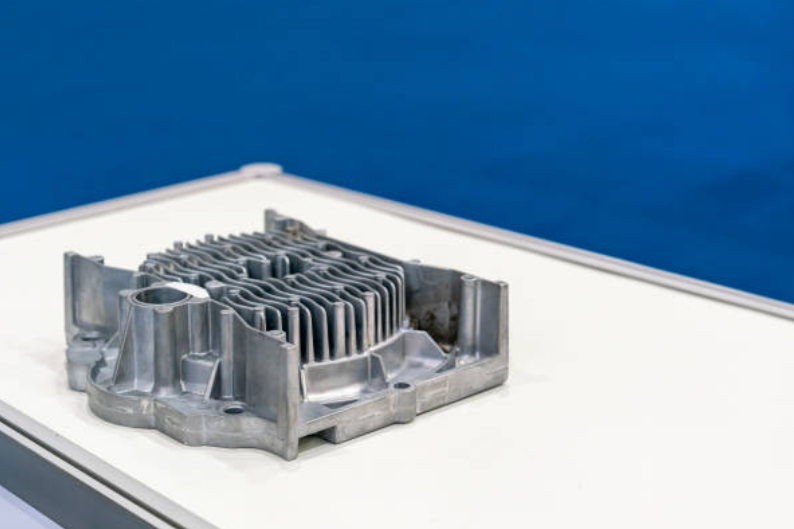
Zinc Die Casting | Process, Materials, Benefits, Applications
In the vast landscape of manufacturing processes, one method stands out for its versatility, precision, and efficiency: zinc die casting. This blog explores the world of zinc die casting and its significance in meeting the needs of buyers and part design engineers seeking custom zinc die-casting parts or services.
A brief overview of zinc die casting
Zinc die casting is a manufacturing process that involves injecting molten zinc alloy into a custom-designed mold, resulting in intricate and highly detailed components. Zinc die casting has gained popularity due to its exceptional dimensional accuracy and ability to produce complex shapes with tight tolerances. Zinc alloy materials have a low melting point, are easy to die-cast and machine, and have excellent surface treatment properties. Zinc alloy also has a higher density, which increases the texture of zinc alloy parts. This is not available in other high-density alloys and die-casting aluminum alloys.
Importance of zinc die casting in manufacturing
Zinc die casting plays a vital role in the manufacturing industry, offering many benefits that make it a preferred choice for various applications. Its versatility, cost-effectiveness, and ability to produce high-quality parts with excellent surface finishes make it indispensable in various sectors.
Zinc Die Casting Process Step by Step
The zinc die-casting process involves several steps to produce reliable and consistent parts. It begins with the preparation of the mold, followed by the melting of the zinc alloy and the injection of the molten metal into the mold cavity. Once cooled and solidified, the part is ejected from the mold, trimmed, and finished to meet the desired specifications.
Design and Mold Preparation
Parts Design
Begin by designing the component or part that you want to produce. This involves creating detailed drawings or computer-aided design (CAD) models, including 3D and 2D drawings. Contact Neway for free design work for die-casting parts.
Molde Building
Once the design is finalized, a mold or die is created. The mold is typically made of steel and consists of two halves, the "die" and the "cover die," which can be opened and closed.
Preparing the Die Casting Machine
The die-casting machine is set up and prepared for operation. This includes heating the machine and the die to the required temperature.
At the stage of preparing the die-casting machine. We must design the mold and choose a zinc alloy die-casting machine with a suitable tonnage according to the size of the zinc alloy parts and the number of mold cavities.
Melting the Zinc Alloy
The zinc alloy, usually a combination of zinc with small amounts of aluminum, copper, and other metals, is melted in a furnace at a specific temperature. The melting point of zinc alloy is relatively low, which allows us to save costs in the metal smelting process. It also makes zinc alloys easier to process.

Injection
- The molten zinc is injected into the die-casting machine.
- The die casting machine consists of two platens. The first platen holds the fixed die, while the second platen holds the cover die.
- The molten zinc is injected into the cavity between the two dies under high pressure. The pressure helps ensure the molten metal fills the cavity and creates a precise shape.
Cooling and Solidification
- After injecting molten metal, the dies are held closed while the metal cools and solidifies inside the mold.
- The cooling time depends on the thickness and complexity of the part being produced.
Opening the Dies
- The dies are opened once the metal has solidified and cooled sufficiently, revealing the solidified zinc component.
- The component may still have excess material or flash around the edges, which is removed in the next step.
Trimming and Finishing
- The excess material or flash is trimmed off the component using various cutting tools or methods.
- Additional finishing processes, such as CNC machining, grinding, or polishing, may be employed to achieve the desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
Inspection and Quality Control

- The finished zinc die-cast component undergoes a thorough inspection to meet the required specifications and quality standards.
- This may involve dimensional measurements, visual inspections, and functional testing.
Zinc die casting is known for its exceptional precision, allowing for the production of intricate parts with tight dimensional tolerances. The process enables the creation of complex geometries and thin-walled sections that would be challenging or costly to achieve using other manufacturing methods. Furthermore, zinc die casting offers high production efficiency, allowing for the rapid creation of large quantities of parts within tight timeframes.
Materials Used in Zinc Die Casting
Zinc alloys are the primary materials utilized in the die-casting process. The most commonly used zinc alloy is Zamak 3, which is composed of zinc alloyed with aluminum, magnesium, and copper. Other zinc alloys, such as ZA-8 and Zamak 7, offer specific properties suitable for different applications.
Common Die Casting Zinc Alloys
Material Classification | Material Grade | Applicable Process | Datasheet |
Zinc Alloy | Zamak 3 | Die Casting | |
Zinc Alloy | Zamak 5 | Die Casting | |
Zinc Alloy | Zamak 2 | Die Casting | |
Zinc Alloy | Zamak 7 | Die Casting | |
Zinc Alloy | ZA-8 | Die Casting |
Consideration in selecting the right zinc alloys
Several factors come into play when choosing a zinc alloy for a particular application. These include mechanical requirements, environmental conditions, and aesthetic considerations. The expert guidance of a reputable zinc die-casting service provider can help identify the most suitable alloy that meets the specific needs of each project. You can also use Neway Material Selector to compare and choose suitable materials.
Advantages of Zinc Die Casting
High precision and dimensional accuracy
One of the key advantages of zinc die casting is its ability to achieve high precision and dimensional accuracy. The process allows for tight tolerances, ensuring the final parts meet the required specifications. This level of precision is crucial in industries where precise fit and functionality are paramount.
Excellent surface finish and aesthetic appeal
Zinc die casting offers exceptional surface finish options, making it ideal for parts that require a visually appealing appearance. The process allows for the creation of smooth surfaces, intricate details, and textures, enhancing the overall aesthetics of the final product. Zinc die casting can deliver the desired visual impact, whether it's a polished finish or a specific texture.
Superior strength and durability
Despite its lightweight nature, zinc die casting produces remarkable strength and durability parts. Zinc alloys possess excellent mechanical properties, offering high tensile strength and impact resistance. This makes zinc die castings suitable for applications where structural integrity and longevity are crucial factors.
Cost-effectiveness and production efficiency
Zinc die casting provides cost-effective solutions for manufacturing custom parts. The high-speed production capabilities of the process enable large quantities of parts to be produced quickly, reducing production costs per unit. Additionally, the longevity and reliability of zinc die castings minimize maintenance and replacement expenses over time.
Applications of Zinc Die Casting
Automotive industry
The automotive industry extensively utilizes zinc die casting for various components. From engine brackets to transmission housings, zinc die-cast parts offer the necessary strength, precision, and cost-effectiveness the automotive sector requires. The process enables the production of lightweight parts without compromising performance.

Electronics industry
In the electronics industry, zinc die casting is vital in manufacturing connectors, housings, and other components. The process offers excellent electromagnetic shielding properties, ensuring the integrity of sensitive electronic devices. The ability to create intricate designs and tight tolerances makes zinc die casting suitable for miniaturized electronic components.
Consumer goods industry
Zinc die casting finds widespread use in the consumer goods industry, providing high-quality parts for locks, hardware, and decorative elements. The versatility of the process allows for the production of intricate and aesthetically pleasing designs that enhance the appeal of consumer products. The durability and corrosion resistance of zinc alloys ensure the longevity of these components.
Other industries benefiting from zinc die casting
Zinc die casting caters to industries beyond automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. It finds applications in aerospace, plumbing, medical devices, and more. The versatility of zinc alloys, combined with the cost-effectiveness and high-quality results of the process, makes it a preferred choice across diverse industries.
Disadvantages of Zinc Die Castings
While zinc die castings offer numerous advantages. It's important to consider potential drawbacks associated with the process. Understanding these limitations can help make informed decisions regarding using zinc die castings for specific applications.
Limited temperature resistance
One of the primary disadvantages of zinc die castings is their limited temperature resistance compared to other materials like steel or aluminum. Zinc alloys have a relatively low melting point, typically around 400°C (752°F). This restricts their use in high-temperature applications where materials with higher melting points may be required.
Potential for surface porosity
Zinc die castings are susceptible to surface porosity, which refers to the formation of small voids or pores on the part's surface. These pores can affect the part's appearance and may compromise its structural integrity if they occur in critical areas. Proper mold design, process control, and surface treatment techniques can help minimize the occurrence of surface porosity. For example, oil-sprayed zinc alloy parts will peel after long-term use, causing the protective layer to fall off.
Limited size and weight capabilities
Compared to other casting processes, zinc die casting has limitations regarding the size and weight of the parts that can be produced. Large and heavy components may pose challenges in mold design, material flow, and ejection from the mold. Alternative manufacturing methods, like sand casting or investment casting, may be more suitable for such applications.
Higher tooling costs for complex geometries
Zinc die casting requires intricate molds to produce complex geometries with high precision. The design and fabrication of these molds can be more costly than simpler molds used in other casting processes. Complex part geometries, including undercuts and thin-walled sections, add complexity to the tooling design, increasing both tooling and production costs.
Environmental considerations
While zinc alloys used in die casting are recyclable, the process requires energy-intensive operations such as melting and casting. Proper waste management and recycling practices are essential to minimize the environmental impact of zinc die casting. It is crucial to work with reputable service providers, prioritizing sustainable manufacturing practices and having effective recycling systems in place.
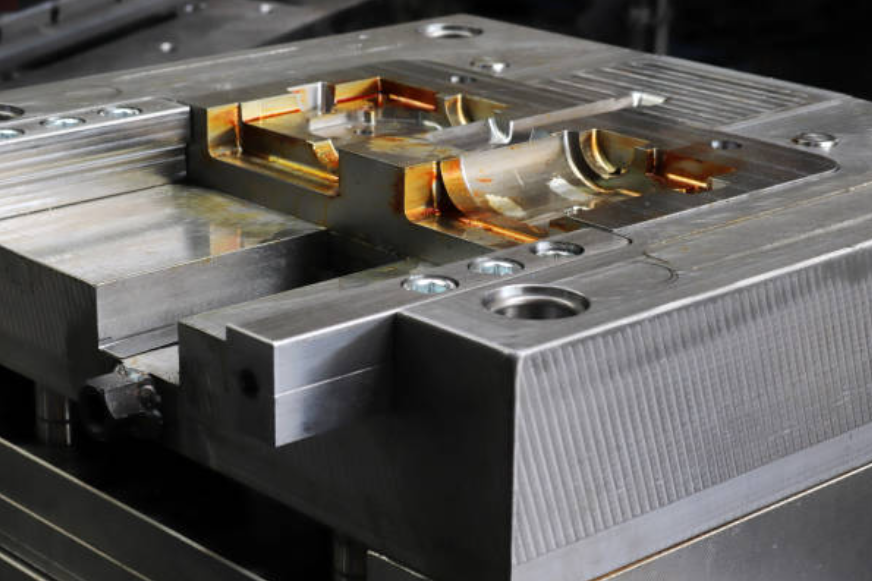
How to Choose a Reliable Zinc Die Casting Service
Factors to consider when selecting a service provider
When selecting a zinc die casting service provider, several factors should be considered. These include the provider's experience and expertise in zinc die casting, reputation, and track record, the range of services offered, and ability to meet specific project requirements. Collaborating with a knowledgeable and reliable partner ensures the successful execution of zinc die casting projects.
Quality assurance and certifications to look for
Quality assurance is paramount when it comes to zinc die casting. Look for service providers with stringent quality control processes, such as ISO 9001 certification. Additionally, certifications specific to the industry, such as IATF 16949 for the automotive sector, demonstrate a commitment to maintaining high standards throughout manufacturing.
Importance of expertise and experience in zinc die casting
Zinc die casting is a specialized field that requires expertise and experience for optimal results. Partnering with a service provider with in-depth knowledge of zinc alloys, mold design, and process optimization ensures the project is executed flawlessly. Experienced professionals can offer valuable insights and recommendations, from material selection to final production.
Neway Introduction
Neway has focused on the customization of metal and plastic parts for 30 years. We have a strong design team, production department, and quality control system. If you are looking for a reliable zinc alloy die casting supplier, don't hesitate to get in touch with us.