Streamlining Success: Enhancing Efficiency in Custom Metal Bending Operations
Introduction
Custom metal bending is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, essential in the automotive, aerospace, construction, and consumer electronics sectors. This process shapes metals into precise forms to achieve specific functions and structural integrity. Enhancing efficiency in metal bending accelerates production and lowers costs, whether manufacturers utilize methods such as CNC precision machining or apply specialized surface finishes, like anodizing.
Understanding Custom Metal Bending
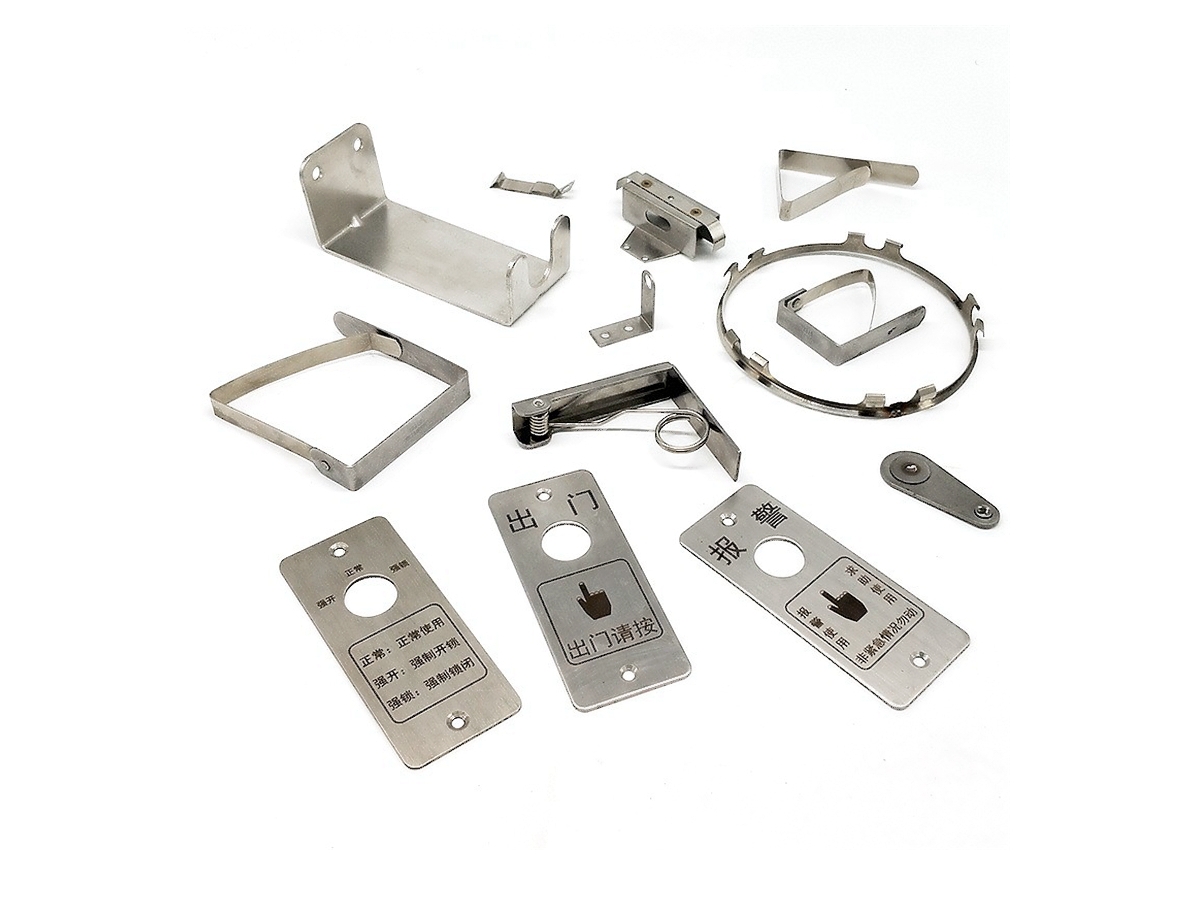
Metal bending involves deforming metals into accurate angles and shapes through controlled mechanical forces. It is fundamental in manufacturing a wide range of products, from simple brackets and structural supports to complex components used extensively in industries such as automotive manufacturing. The versatility and precision of this process allow the production of components with enhanced durability, structural integrity, and optimal functionality.
Key Factors for Efficient Metal Bending
Material Selection
Choosing suitable materials is crucial to efficient metal-bending operations. Metals like aluminum, stainless steel, carbon steel, copper, and advanced alloys like Inconel each possess unique bending characteristics. Selecting appropriate materials based on performance criteria helps manufacturers minimize common issues such as cracking, deformation, and spring-back, ultimately streamlining the production process.
Tooling and Equipment Maintenance
Maintaining high-quality equipment and tooling ensures consistent results and reduces downtime in metal bending operations. Regular inspections and preventive maintenance significantly enhance precision and reliability. Employing specialized consultative mechanical design services can further optimize tooling performance and equipment longevity.
Operator Training and Skill Development
Effective operator training is crucial for maintaining high standards of accuracy, consistency, and productivity. Skilled operators proficient in modern bending methods, such as rotary draw bending, can efficiently manage complex geometries, minimize errors, and consistently deliver high-quality outcomes, thereby directly influencing productivity and profitability.
Technological Innovations Enhancing Efficiency
CNC Metal Bending Machinery
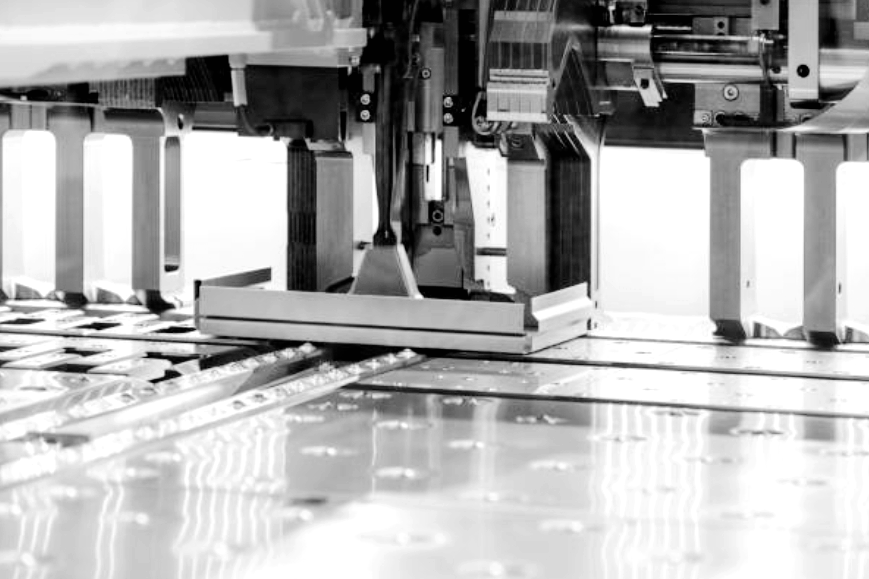
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology revolutionizes metal bending through unmatched accuracy, repeatability, and speed. CNC systems precisely control bending angles and sequences, greatly reducing the manual adjustments required and significantly cutting down setup times. The integration of CNC technology has enabled manufacturers to produce complex components with consistent, tight tolerances, particularly in sectors such as aerospace component manufacturing.
Automated and Robotic Systems
Incorporating automation and robotics into metal-bending operations dramatically enhances production efficiency. Robotic bending solutions reduce manual labor, minimize human error, and enhance workplace safety. Industries that adopt these technologies, notably the automotive and consumer electronics sectors, experience increased throughput, improved accuracy, and streamlined production workflows.
Integrated Software Solutions
Advanced bending software significantly boosts efficiency by precisely predicting material behaviors, optimizing bend sequences, and minimizing material waste. Integrating software systems with existing machinery enables streamlined workflows, more accurate production forecasting, and reduced lead times, which is particularly beneficial when working with demanding materials, such as special alloys.
Optimizing Processes for Maximum Efficiency
Streamlined Workflow Management
Effective workflow management is central to enhancing metal-bending operations. Systematic organization of workspace, precise scheduling, and optimized task sequencing eliminate bottlenecks, decrease production interruptions, and improve overall workflow continuity. These optimizations foster an environment of increased productivity, lower operational expenses, and sustainable efficiency.
Waste Reduction through Precise Material Usage
Implementing advanced simulation software and precise material calculations can significantly reduce material waste. Minimizing scrap metal and achieving optimal raw material usage aligns with eco-friendly manufacturing strategies, directly benefiting both environmental sustainability and overall production cost efficiency.
Real-World Examples of Enhanced Efficiency
Automotive Industry Application
A leading automotive parts manufacturer integrated automated robotic bending into their processes, substantially increasing productivity. Robotics streamlined operations, reduced manual errors, and optimized workflow, demonstrating significant improvements in throughput, consistency, and overall production quality.
Aerospace Industry Innovation
An aerospace manufacturer successfully adopted CNC bending technologies coupled with software-driven precision. This enabled efficient handling of high-tolerance materials such as titanium and Haynes alloys, substantially reducing errors and improving delivery timelines.
Overcoming Common Bending Challenges
Spring-back Management
Spring-back presents a common challenge in bending high-strength metals. Operators mitigate this issue through careful overbending, specialized tooling, and the use of predictive bending software to anticipate and accurately adjust bend angles.
Addressing Material Cracking
Material cracking, a common issue in brittle metals, can be avoided by preheating the metal, using gradual bending techniques, or selecting more ductile materials, such as certain nickel-based alloys.
Minimizing Deformation
Controlling deformation in soft or thin materials, such as aluminum, involves carefully designed tooling and supportive dies to distribute stress evenly. Techniques inspired by high-precision die casting processes can effectively reduce deformation risks.
Conclusion
Enhancing efficiency in custom metal bending involves strategic material selection, technological innovations such as CNC machinery and robotics, and optimizing operational processes. Companies adopting these advancements streamline production, significantly reduce operational costs, enhance precision, and strengthen their competitive edge, positioning themselves for sustained growth and success.