Securing Success: How Insert Molding Improves Reliability in Component Design
Introduction
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, ensuring the reliability of components is crucial. Techniques like insert molding significantly enhance component performance and reliability by integrating pre-formed inserts directly into molded parts. Widely used in sectors such as automotive, consumer electronics, and medical devices, insert molding streamlines manufacturing processes, delivering robust, durable, and cost-effective solutions.
What is Insert Molding?
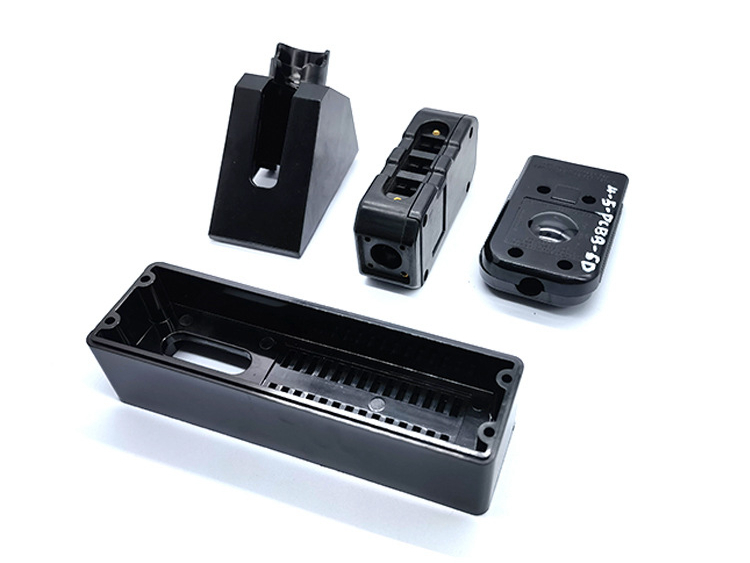
Insert molding is a specialized form of plastic injection molding wherein pre-made metal or plastic inserts are placed into a mold. Molten plastic, commonly ABS, nylon, or polycarbonate, is injected around these inserts. Upon cooling, the result is a single, robust component with enhanced strength and functionality, eliminating traditional assembly steps.
Unlike traditional assembly processes, insert molding delivers higher precision, increased structural integrity, and significant time and cost savings.
Advantages of Insert Molding for Component Reliability
Enhanced Structural Integrity
Insert molding substantially increases the durability of components by embedding strong metal inserts—often brass, steel, or aluminum—into plastics like nylon. This method improves resistance to vibration, shock, and mechanical stresses, which is essential for demanding applications in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Reduced Assembly Complexity and Costs
By consolidating multiple manufacturing operations into one seamless process, insert molding significantly reduces assembly time and labor costs. This streamlining directly benefits manufacturers in high-volume production scenarios, boosting productivity while ensuring consistent quality.
Precision and Consistency
Insert molding achieves excellent repeatability due to the precise placement of inserts and controlled injection parameters. This consistency ensures each produced part meets stringent dimensional tolerances, which is vital in industries such as medical devices and electronics, where reliability and accuracy are paramount.
Scalability and Cost-Effectiveness
Although initial setup costs may be notable, insert molding quickly offsets these expenses in mass production. High-volume output drastically reduces per-unit costs, making insert molding highly cost-effective, particularly when maintaining rigorous quality standards is necessary.
Applications and Industry Examples
Automotive Industry
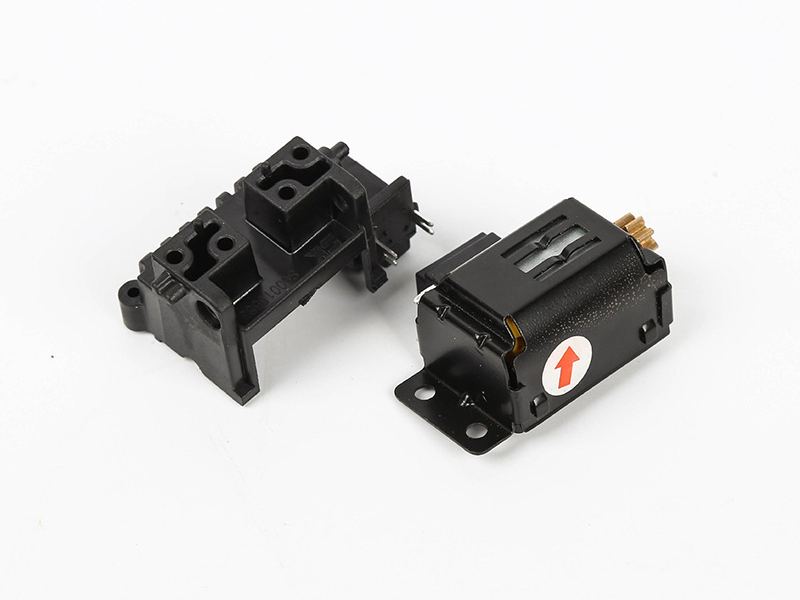
Automotive manufacturers frequently use insert molding to produce metal-reinforced connectors, sensor housings, and electrical components. This ensures improved durability, reduced weight, and heightened reliability—critical for automotive safety and performance.
Medical Device Manufacturing
In the medical industry, insert molding is used extensively for products requiring exceptional precision, including surgical instruments, catheter fittings, and diagnostic tools. Combining metal inserts with medical-grade plastics such as polycarbonate delivers reliable, sterile, and consistent medical components.
Consumer Electronics
Insert molding produces robust connectors, housings, and reinforced components essential for smartphones, laptops, and home appliances. Using durable inserts combined with plastics like ABS ensures extended device lifespan, reliability, and customer satisfaction.
Real-World Case Studies Highlighting Reliability
Automotive Sensor Housings
A leading automotive supplier integrated brass inserts with nylon housings through insert molding, achieving a 30% increase in mechanical durability and a notable reduction in manufacturing defects, ultimately enhancing vehicle reliability.
Electronics Connectors
An electronics manufacturer utilized insert molding to produce connectors, embedding aluminum inserts within ABS casings. The result was a 25% improvement in product lifespan, fewer warranty issues, and reduced manufacturing costs, reinforcing consumer trust and brand reputation.
Best Practices for Implementing Insert Molding Successfully
Precision Mold and Insert Design
Precise mold design and insert alignment are critical for ensuring consistent product quality. Accurate placement of inserts within molds guarantees structural integrity and reliability across production batches.
Strong Material Compatibility and Adhesion
Material compatibility is essential to successful insert molding. Selecting compatible insert materials, like brass or stainless steel, and plastics, such as ABS, ensures robust adhesion and long-lasting durability.
Automation for Enhanced Efficiency
Employing automated insert placement and robotics reduces human error, enhances production consistency, and improves overall efficiency. Automation helps manufacturers maintain consistent quality and reliability, even in high-volume scenarios.
Addressing Common Challenges in Insert Molding
Material Compatibility Issues
Selecting compatible materials, such as combining brass inserts with plastics like polycarbonate, ensures robust bonding and prevents potential component failures.
Managing Cost-Effectiveness
Strategically planning high-volume insert molding production allows manufacturers to recover initial investments quickly. Efficient mold design and process automation further enhance long-term profitability.
Consistency in Production Quality
Implementing rigorous quality assurance protocols, frequent inspections, and predictive maintenance prevents defects and ensures consistent, reliable component production over time.
Future Trends in Insert Molding Reliability
Innovations in Material Technology
Emerging materials such as high-performance polymers, hybrid composites, and sustainable plastics promise even greater strength, reliability, and cost efficiency, expanding insert molding applications into new industries and applications.
Smart and Integrated Technologies
Integrating smart sensors and embedded electronics within insert-molded components represents a significant future trend. This integration is especially relevant for industries like e-mobility and telecommunications, where multifunctionality and reliable performance are critical.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Increasingly, manufacturers prioritize sustainable and recycled materials within insert molding processes, enhancing both environmental responsibility and economic efficiency, aligning with global sustainability initiatives.
Conclusion
Insert molding significantly enhances component reliability, precision, and manufacturing efficiency, offering substantial benefits across automotive, medical, and consumer electronics sectors. Companies leveraging insert molding technology strategically enhance product performance, reduce costs, and gain long-term competitive advantages, ensuring their success in today’s demanding market environment.
FAQs:
What types of materials are most suitable for insert molding?
How does insert molding improve the reliability of components?
What industries benefit most from insert molding?
Can insert molding reduce production costs compared to traditional methods?
What are the common challenges in insert molding and how can they be resolved?