Precision and Efficiency: The Role of Laser Cutting in Fabrication
Introduction
Laser cutting is an advanced manufacturing technique widely used for precise and efficient fabrication. This technology ensures unparalleled accuracy, speed, and versatility by employing focused laser beams for cutting, engraving, or marking. The growing need for precision manufacturing in sectors like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical device production highlights laser cutting’s critical role in modern fabrication processes.
1. Understanding Laser Cutting
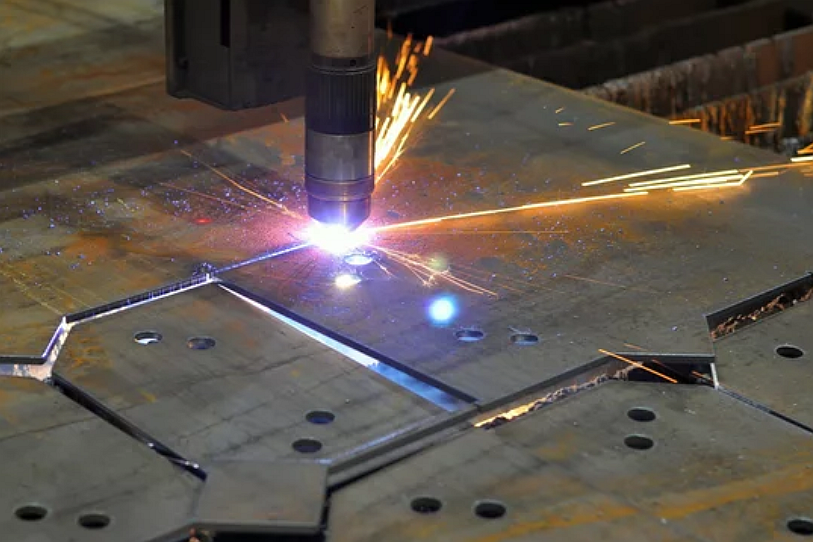
Laser cutting employs coherent, focused beams of light to cut or engrave materials through melting, burning, or vaporization, guided by precise computer-controlled systems.
Types of Lasers Commonly Used:
CO₂ Lasers: Utilizing carbon dioxide gas, these lasers effectively cut and engrave non-metals like acrylic, wood, plastics, textiles, and leather, offering high-quality surface finishes.
Fiber Lasers: Employ fiber optic cables with rare-earth elements, ideal for metals like stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and brass, providing excellent precision in metal fabrication processes.
Nd:YAG Lasers: Utilize neodymium-doped crystals, commonly applied in precise metal cutting and welding.
Key Elements of Laser Cutting Systems:
Laser resonator
Cutting head with focusing lens
CNC control systems
Motion control systems (motors and axes)
Assist gas delivery systems
2. Advantages of Laser Cutting in Fabrication
Laser cutting delivers distinct benefits, ideal for precision fabrication:
Exceptional Precision and Accuracy: Tight tolerances reduce secondary machining, ensuring consistently high-quality outputs ideal for complex industrial components.
High Cutting Speeds and Productivity: Rapid production cycles significantly enhance throughput and efficiency, which is beneficial for industries like automotive manufacturing.
Minimal Material Wastage: Precise laser cutting reduces scrap, optimizes material use, and enhances cost efficiency and sustainability in production.
Versatility Across Various Materials: Laser cutting processes diverse materials—from metals and plastics to composites and textiles—making it adaptable to various manufacturing applications.
3. Applications of Laser Cutting in Manufacturing
Laser-cutting technology significantly supports numerous industries through precision and efficiency:
Automotive Components: Precisely cuts automotive parts, including chassis components, engine parts, interior trims, and decorative fittings, ensuring accuracy and consistency for high-volume automotive production.
Aerospace and Aviation Industry: Precision laser cutting of aerospace components such as turbine blades, avionics housings, and structural parts meets stringent safety and quality standards in aerospace manufacturing.
Electronics and Telecommunications: Produces intricate shapes in PCBs, electronic enclosures, and connectors, ensuring accuracy required by the electronics sector.
Medical Device Manufacturing: Achieves the necessary precision in implants, surgical tools, and diagnostic components, fulfilling stringent medical industry requirements.
Metal and Non-Metal Fabrications: Serves general manufacturing by efficiently fabricating custom metal components, architectural models, signage, and decorative elements with consistent quality and speed.
4. Comparing Laser Cutting with Other Fabrication Techniques
To appreciate laser cutting's unique benefits, comparing it with alternative techniques is essential:
Laser Cutting vs. Mechanical Cutting (Sawing, Punching):
Mechanical methods involve physical contact and tool wear, potentially compromising precision. Laser cutting is contactless, providing superior accuracy, cleaner edges, and eliminating tool wear, which is crucial in high-precision machining.
Laser Cutting vs. Plasma Cutting:
Plasma cutting excels in thicker metal sheets but lacks laser cutting's precision and edge quality. Laser cutting provides finer details and minimal kerf width, ideal for intricate, thinner metal parts.
Laser Cutting vs. Waterjet Cutting:
Waterjet cutting suits heat-sensitive materials but operates slower. Laser cutting offers faster speeds and greater production efficiency, which is particularly beneficial for high-volume manufacturing.
Deciding Factors for Choosing Laser Cutting:
Precision requirements
Material type and thickness
Production volume
Budget constraints
Desired finish quality
5. Challenges and Solutions in Laser Cutting
Laser cutting, despite numerous advantages, presents certain challenges:
Heat Distortion: Excess heat may warp materials. Solutions include optimizing cutting parameters, employing pulsed laser modes, and improving assist gas flow to dissipate heat effectively.
Material Limitations: Reflective metals like aluminum and copper may pose challenges. Utilizing fiber lasers or specialized coatings can effectively manage these reflective properties.
Kerf Width: Precision can be affected by kerf width. Minimizing this involves carefully adjusting laser focus, controlling power settings, and selecting suitable optics to maintain tight tolerances and accurate finishes.
Addressing these issues ensures consistent quality and productivity in laser-cutting operations.
Conclusion
Laser cutting is critical in contemporary manufacturing, delivering unmatched precision, efficiency, and adaptability. Its ability to rapidly produce accurate, intricate components across various materials and industries makes laser cutting essential for remaining competitive and meeting stringent industry standards. Manufacturers seeking enhanced productivity, reduced material waste, and consistently high-quality outcomes should integrate laser cutting technology into their fabrication processes to maximize its benefits.
FAQs:
What types of materials can be processed using laser cutting?
How does laser cutting achieve such high precision?
What are the main differences between CO₂ and fiber laser cutting?
Why is laser cutting preferred over mechanical cutting in precision manufacturing?
What measures can reduce distortion in laser-cutting processes?