Expanding Industry Applications of 3D Printed Parts in Modern Manufacturing
Introduction
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is transforming modern manufacturing by enabling unprecedented levels of customization, efficiency, and innovation. By building components layer by layer from digital designs, industries can achieve intricate structures and highly tailored solutions impossible with traditional manufacturing techniques. This versatility drives widespread adoption across numerous sectors, reshaping manufacturing processes, and opening doors to new possibilities.
1. Aerospace and Aviation
The aerospace industry has been among the earliest adopters of 3D printing, leveraging its capabilities to enhance aircraft performance, reduce weight, and increase production flexibility.
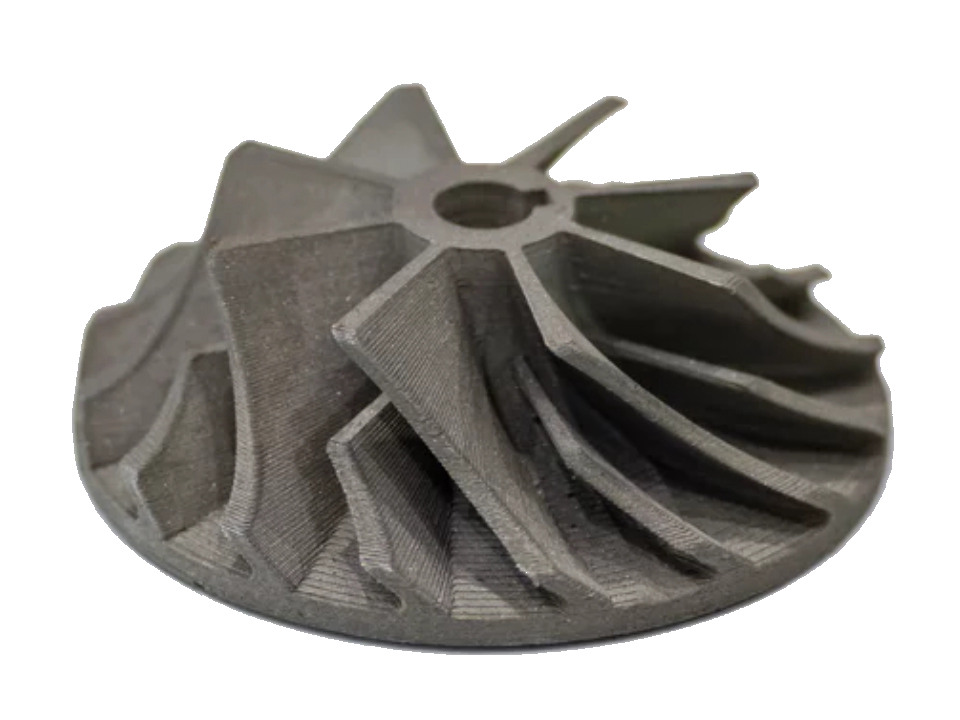
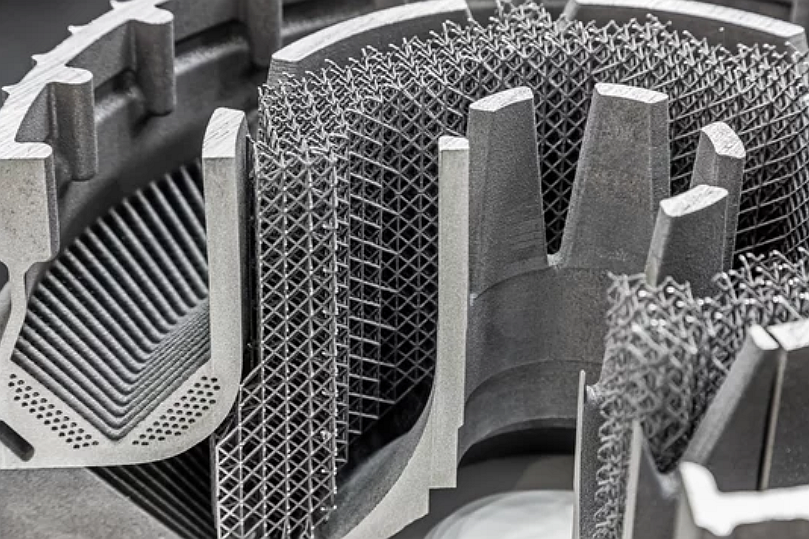
Complex structural components
3D printing allows aerospace manufacturers to produce complex, lightweight structures such as turbine blades, heat exchangers, and high-performance engine components with precise specifications, significantly reducing aircraft weight and enhancing fuel efficiency.
Rapid prototyping and testing
Additive manufacturing accelerates prototyping, enabling aerospace engineers to test quickly and iterate designs, substantially reducing development cycles and costs and ensuring faster market entry.
Custom and replacement parts
The ability to rapidly produce custom parts on demand reduces downtime and inventory costs, providing aerospace industries the flexibility to address maintenance needs and streamline supply chains efficiently.
2. Medical and Healthcare
Healthcare significantly benefits from 3D printing, enhancing patient care with highly personalized medical solutions.
Custom prosthetics and implants
3D printing facilitates the production of patient-specific prosthetics and implants tailored precisely to individual anatomies, often employing biocompatible materials such as titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V), greatly improving patient outcomes and comfort.
Patient-specific surgical guides
Surgeons utilize precise 3D-printed surgical guides, derived from patient scans, to increase accuracy and reduce procedure times, significantly improving surgical precision and reducing complications.
Bioprinting advancements
Innovations in bioprinting technology offer immense potential for creating functional biological tissues and organs, paving the way for breakthroughs in regenerative medicine and organ transplantation.
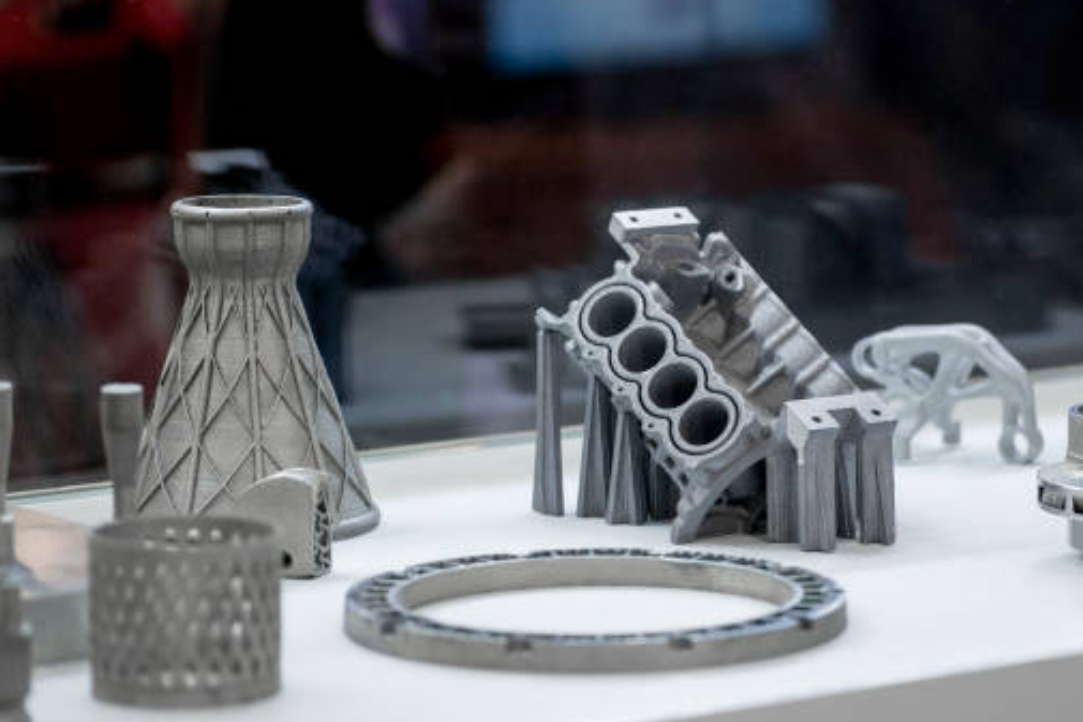
3. Automotive Industry
The automotive sector extensively benefits from additive manufacturing, facilitating rapid development, custom manufacturing, and performance optimization.
Rapid prototyping and product development
Automotive manufacturers employ 3D printing for prototyping new components, significantly shortening the design-to-production timeline. This accelerates concept testing, reduces costs, and enhances final product quality.
Customized parts and components
3D printing enables creation of highly customized automotive parts such as personalized interior features, customized vehicle accessories, and replacement parts, effectively expanding market opportunities.
Lightweighting strategies and improved efficiency
Additive manufacturing supports light weighting in automotive design, improving fuel efficiency, reducing emissions, and improving vehicle performance. Structural parts, brackets, and heat exchangers commonly utilize lightweight materials like cast aluminum alloys.
4. Consumer Goods and Electronics
Consumer goods and electronics industries leverage 3D printing to swiftly respond to changing consumer demands and market trends.
Custom products and personalized solutions
From customized jewelry and tailored eyewear to personalized consumer electronics, 3D printing allows businesses to rapidly produce unique products, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Prototype and concept validation
3D printing accelerates product development by quickly validating design concepts and functional prototypes, significantly reducing time to market for new products.
Small-batch manufacturing
Additive manufacturing economically produces small batches of highly customized electronic components and niche products, circumventing traditional manufacturing’s high setup costs.
5. Construction and Infrastructure
The construction industry uses 3D printing to enhance productivity, reduce waste, and foster architectural innovation.
Construction components
3D printing facilitates production of concrete structures, walls, and modular components, drastically reducing construction timelines and labor costs, while promoting sustainable material usage.
Architectural design flexibility
Architects use additive manufacturing to execute innovative and complex building designs previously challenging with traditional methods, encouraging architectural creativity.
Sustainable building practices
3D printing reduces material waste, enhances construction speed, and supports environmentally friendly building methods through optimized resource usage, contributing to sustainability goals.
6. Energy and Renewable Resources
3D printing greatly benefits renewable energy and power generation sectors, enhancing efficiency and reliability.
Renewable energy components
Additive manufacturing produces critical renewable energy components like wind turbine blades, solar panel brackets, and battery storage units with enhanced strength, reduced weight, and optimized performance efficiency.
Custom battery housings
Energy storage systems leverage customized 3D-printed battery housings, improving safety, thermal management, and overall system reliability.
Performance optimization
3D printing enables the creation of components with optimized geometries for improved energy efficiency, reduced maintenance needs, and increased operational lifetimes, significantly benefiting energy applications.
Conclusion
3D printing continues to drive profound transformations in modern manufacturing, significantly expanding industrial applications across sectors by offering unparalleled customization, efficiency, and innovation. As the technology matures, the scope of additive manufacturing will inevitably broaden, shaping a more dynamic and responsive manufacturing landscape.
FAQs:
What industries benefit most from adopting 3D printing?
How cost-effective is 3D printing compared to traditional manufacturing methods?
What are the limitations of 3D printing in industrial applications?
Can 3D printed parts achieve the same strength as traditionally manufactured parts?
What materials are commonly used in industrial 3D printing?