Custom Sand Casting | Process, Materials, Pros, and Cons
Sand Casting Process Overview
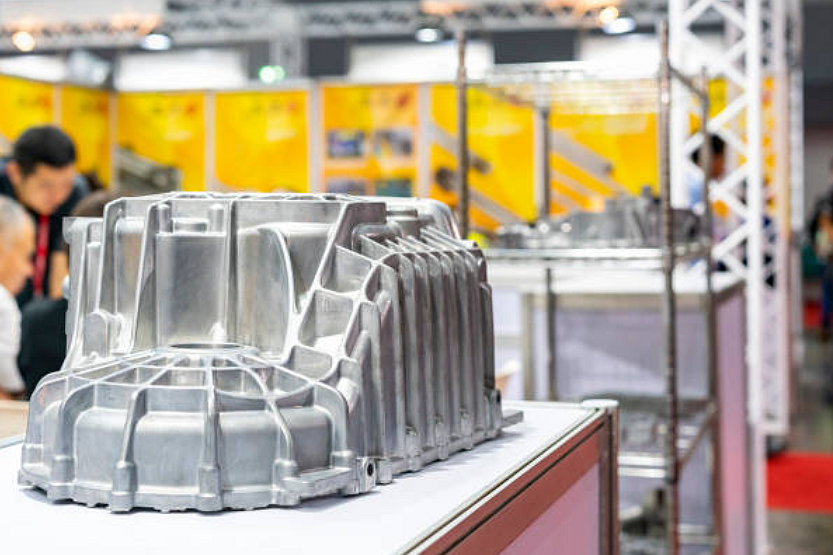
Neway custom sand-casting service is widely used for manufacturing custom parts with various materials, including sand-cast aluminum, sand-cast steel, and more. This process involves several crucial steps that ensure the creation of high-quality castings. Custom sand castings are generally used to manufacture parts with complex structures, small quantities, and large weight or size.
Custom sand casting allows various post-processing treatments, including CNC machining, to achieve the required detail and precision. Use powder coating to get the corresponding surface effect. Heat treatment to enhance the mechanical properties of castings.
Custom sand casting services can choose from various materials, including aluminum alloy, copper alloy, titanium alloy, iron, stainless steel, and other hard alloys. Sand casting has a lower initial mold cost and higher design flexibility than die casting.

Mold Preparation:
Before starting the casting process, meticulous mold preparation is essential. The sand-cast mold serves as a cavity that shapes the final product. The sand cast mold is typically made of sand or sand cast mold, which can withstand the high temperatures required for casting. Sand casting molds offer flexibility and ease of modification, making them ideal for custom part production.
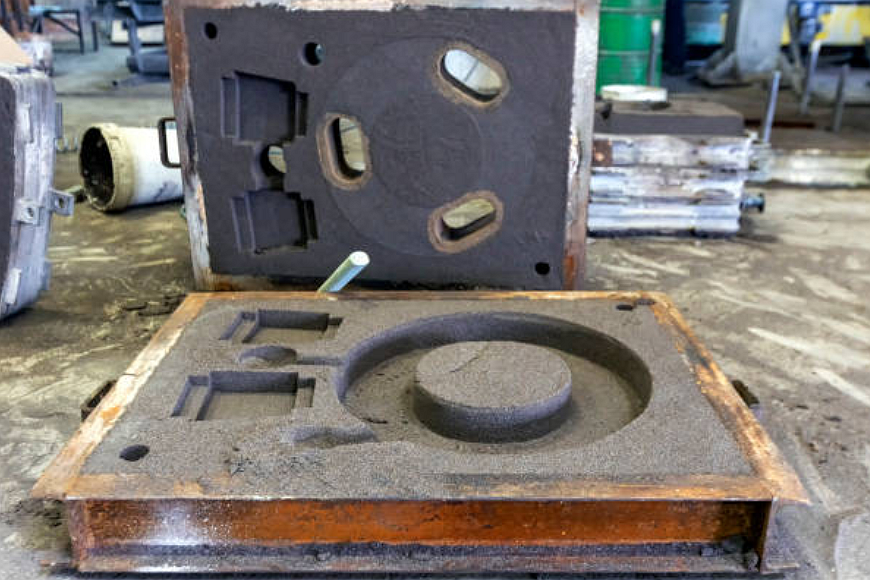

Pattern Creation:
The next step involves creating a pattern, a replica of the desired part. Patterns can be made from wood, plastic, or metal, and they determine the final shape and dimensions of the sand castings. Expert patternmakers ensure precision and accuracy in pattern creation, producing high-quality sand cast parts.
Core Production:
Sand cast foundry in some cases. Complex parts may require the use of sand-cast cores. Cores are additional structures inserted into the mold to create internal cavities or intricate features. Cores are made from sand and other materials, providing support during the casting process. Sand casting complexity is higher than the injection molding and die-casting processes.
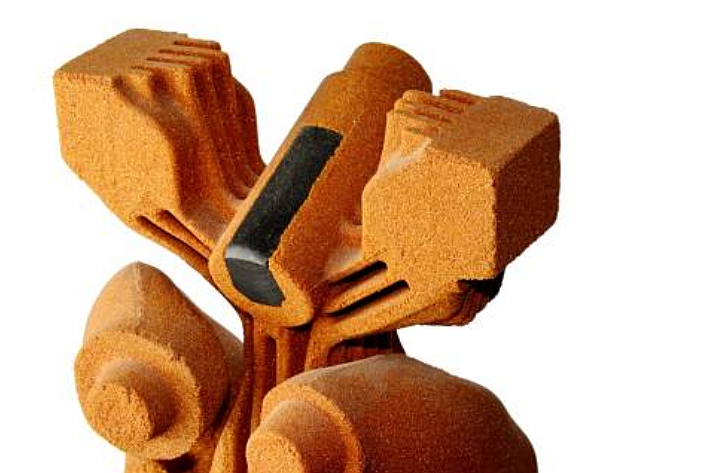

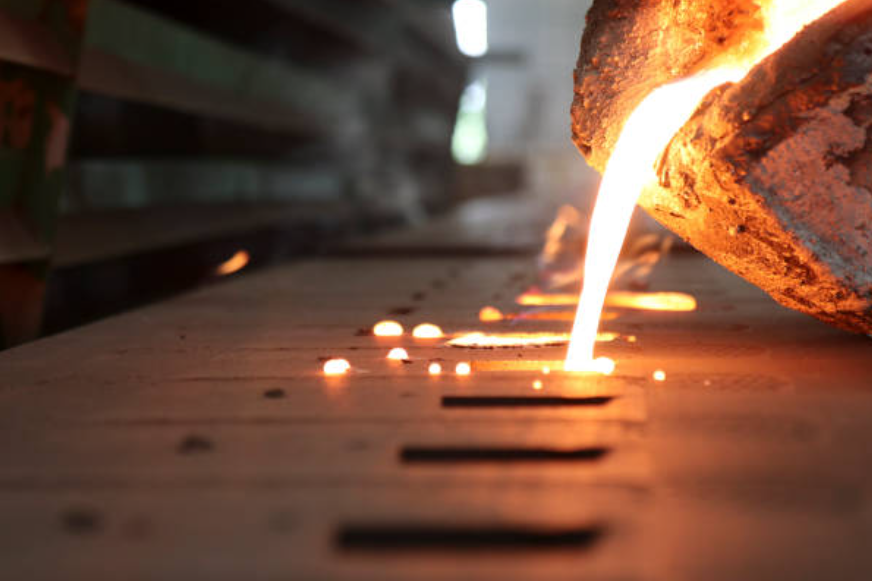
Melting and Pouring:
Once the mold and cores are prepared, the next step is to melt the chosen material, such as sand cast aluminum or sand cast steel. The molten metal is then carefully poured into the mold, ensuring it fills the entire cavity. Proper temperature control and pouring techniques are critical to achieving optimal casting results.
Cooling and Solidification:
After pouring, the molten metal cools and solidifies within the mold. The cooling rate is carefully managed to prevent defects and ensure proper grain structure formation. This step requires patience and precision to achieve the desired mechanical properties.
Casting Finishing:
Once the casting has sufficiently cooled and solidified, it is removed from the mold. However, the casting may require additional finishing processes to achieve the desired surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and overall quality. Finishing techniques such as grinding, sandblasting, machining, and heat treatment may refine the casting to meet specific requirements.
Custom Sand Casting Materials
1. Types of Sand Casting Materials:
The sand casting process offers versatility regarding sand casting material selection. It is compatible with various alloys, including aluminum, steel, bronze, and iron. Among these, sand-cast aluminum and sand-cast steel are widely used due to their desirable properties and availability.
2. Materials Grade Table sheet:
Materials grade tables are used to assist in material selection for sand casting. These tables provide valuable information about different alloys, their mechanical properties, and their suitability for specific applications. Engineers and buyers can refer to these tables to make informed decisions.
3. Other Materials in Sand Casting (Binders, Additives):
In addition to the primary casting materials, sand casting involves using binders and additives. Binders help hold the sand together, ensuring the mold retains its shape during pouring. Additives can enhance mold properties, such as strength and permeability, improving the casting process and the quality of the final part.
4. How to Select Sand Casting Materials:
Selecting the appropriate material for a sand casting project requires careful consideration of factors such as mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and cost. It is essential to understand the specific requirements of the part and consult with experts to determine the most suitable sand casting materials, such as sand casting aluminum alloy, stainless steel, bronze, and iron alloy.
Material Name | Description |
|---|---|
Aluminum alloy with good machinability and corrosion resistance | |
High-pressure aluminum die casting alloy, good fluidity and strength | |
Heat-treatable aluminum alloy, excellent weldability and strength | |
Popular aluminum casting alloy, good balance of properties and cost | |
Surface-treated cast aluminum for improved corrosion resistance and appearance | |
Aluminum alloy with high wear resistance, suitable for engine components | |
General-purpose aluminum casting material | |
Strong, durable, and cost-effective iron alloy for structural and heavy-duty parts | |
Corrosion-resistant stainless steel castings for demanding environments | |
Excellent electrical/thermal conductivity, often used in electrical and heat transfer applications |
Common Sand Casting Surface Treatments:
1. Shot Blasting:
Shot blasting is a widely used surface treatment method for sand castings. It involves propelling small abrasive particles, such as steel shots or grit, at high velocity onto the surface of the casting. This process helps remove surface impurities, scale, and residual sand particles, resulting in a cleaner and smoother surface finish.
2. Grinding and Polishing:
Grinding and polishing are manual or mechanical processes used to refine the surface of sand castings. Grinding involves using abrasive wheels or belts to remove excess material or imperfections, while polishing uses fine abrasives to achieve a smoother and more reflective surface. These processes are often used to improve dimensional accuracy and enhance the aesthetics of the casting.
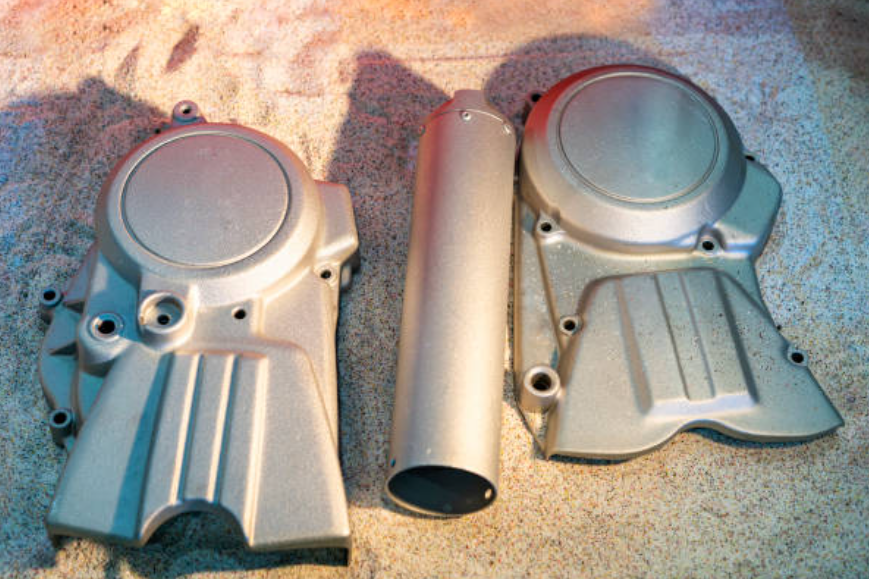

3. Vibratory Finishing:
Vibratory finishing is a mass finishing technique that involves placing sand castings in a vibrating container or bowl filled with abrasive media, such as ceramic or plastic chips, along with water and compounds. The vibrations and media action create a rubbing effect, removing burrs, sharp edges, and surface irregularities. Vibratory finishing can produce a uniform surface finish and improve part functionality.
4. Painting and Powder Coating:
Painting and powder coating are surface treatment methods that enhance the appearance and protect sand castings. Paints and powder coatings are applied to the cleaned and prepared surface of the casting, forming a protective layer that can resist corrosion, wear, and environmental factors. These methods also allow for customization by offering various colors and finishes.
5. Anodizing:
Anodizing is commonly used for sand castings made of aluminum alloys. It is an electrochemical process that creates a controlled oxide layer on the surface of the casting. Anodizing enhances corrosion resistance, improves surface hardness, and can provide decorative finishes. The process involves immersing the casting in an electrolyte bath and applying a current to stimulate the formation of the oxide layer.
6. Heat Treatment:
Heat treatment is another surface method for sand castings. It involves subjecting the casting to controlled heating and cooling processes to alter its mechanical properties. Heat treatment can improve the casting's strength, hardness, and dimensional stability. Standard heat treatment methods for sand castings include annealing, normalizing, quenching, and tempering.
These are some standard die casting surface finish methods used for sand castings. The choice of surface treatment depends on the specific requirements of the casting, such as desired finish, functional properties, and environmental factors. It is essential to consult with experts or surface treatment professionals to determine the most suitable method for a particular sand casting application.
Sand Casting Tolerance Range:
1. Factors that Produce Tolerances:
Tolerances in sand casting refer to the allowable deviation from a part's intended dimensions and specifications. Various factors can affect tolerances, including the part's complexity, the casting process, and the material used. Understanding these factors is crucial in achieving the desired tolerances. Unlike other processing techniques, foundry casting materials tend to have more impurities. Suppose you must use the sand foundry process to produce airtight parts, hydraulic parts, and products with very high surface requirements. In that case, you must communicate with the sand casting foundry beforehand and clarify your requirements.
2. Tolerance Range of Sand Casting:
The tolerance range for sand casting depends on factors such as the part's size and complexity, the foundry's capabilities, and the material being cast. Part design engineers must clearly communicate the required tolerances to the foundry to ensure accurate and satisfactory results.
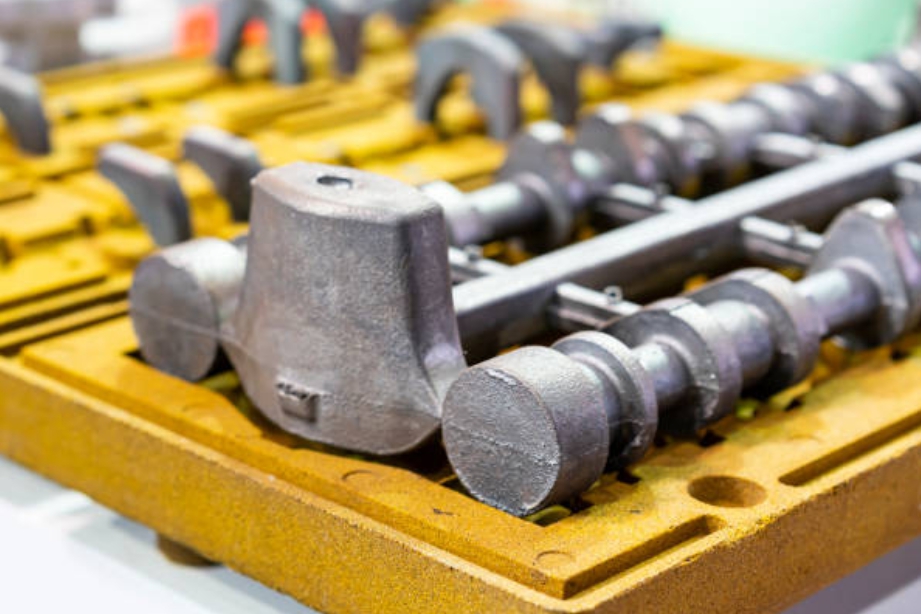

3. Sand Casting Mold Tolerance:
The sand casting process inherently introduces limitations and variations in dimensional accuracy due to mold shifting, pattern wear, and shrinkage. Mold tolerance refers to the acceptable range of deviations that can occur in the mold and affect the final casting. Proper mold design and maintenance play a crucial role in managing mold tolerance.
Highlight the Pros of Sand Casting:
1. Cost-effectiveness for Custom Parts:
Sand casting offers cost advantages, especially for custom parts with complex geometries. The low tooling costs and flexibility in mold creation make it an economical choice for small to medium-production runs. Sand casting eliminates the need for expensive dies or molds, making it a viable option for buyers and part design engineers looking for cost-effective solutions.
2. Design Flexibility and Complexity:
Sand casting allows for intricate and complex designs that may be challenging or costly to produce using other manufacturing methods. The mold can accommodate intricate features, undercuts, and varying wall thicknesses, enabling the creation of highly customized parts. This design flexibility allows engineers to explore innovative solutions and achieve their desired product specifications.
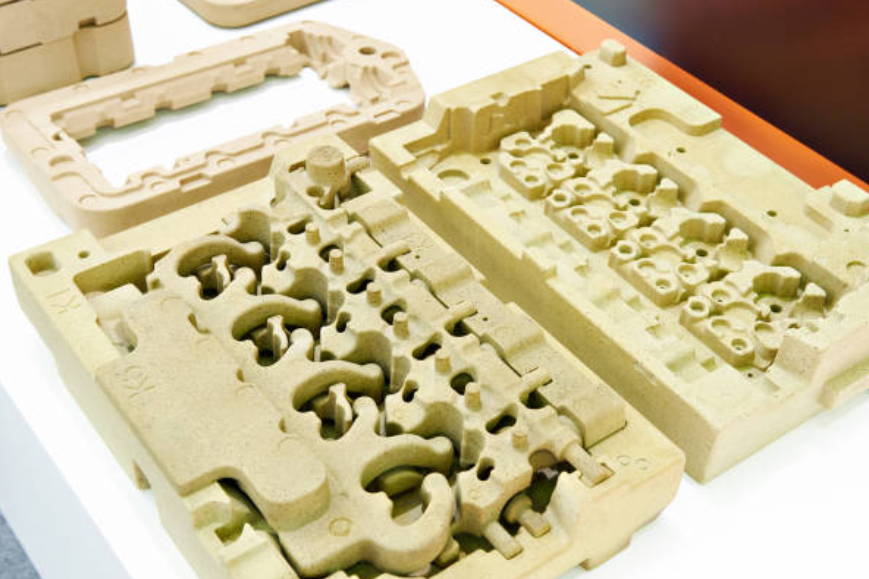

3. Wide Range of Compatible Alloys:
Sand casting is compatible with various alloys, including aluminum, steel, bronze, and iron. This versatility allows for producing parts with specific mechanical properties, such as strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. Sand cast aluminum and sand cast steel, in particular, are popular choices due to their excellent performance in various industries.
4. Suitable for both Small and Large Parts:
Sand casting is suitable for producing parts of varying sizes. Sand casting can accommodate a broad range of small intricate components to significant industrial ones. This versatility makes it ideal for buyers and engineers working on projects with diverse sand casting parts sizes and requirements.
5. Potential for Sustainable Production:
Sand casting is a sustainable manufacturing process due to its minimal material waste. The sand used in the molds can be recycled and reused, reducing environmental impact. The absence of complex tooling and energy-intensive processes further contributes to its sustainability. Sand casting offers an environmentally conscious option for buyers and part design engineers concerned about reducing their carbon footprint.
Cons and Limitations of Sand Casting:
1. Surface Finish and Dimensional Accuracy:
One limitation of sand casting is that it may result in rough surface finishes compared to other precision casting methods. The texture of the sand molds can transfer onto the casting surface, requiring additional finishing operations. Achieving tight dimensional tolerances may also be challenging, particularly for intricate designs.
2. Longer Lead Times for Complex Designs:
The complexity of specific sand-cast parts can lead to longer lead times. The production process involves multiple steps, including mold preparation, pattern creation, and finishing. Complex designs may require additional pattern and mold development time, resulting in extended production timelines.
3. Constraints on Thin-Walled Parts:
Sand casting may have limitations when it comes to producing thin-walled parts. The sand mold needs sufficient thickness to withstand the molten metal's pressure and prevent mold failure during pouring. Thin-walled parts may be prone to defects such as warping or cracking.
4. Small Size Parts Inability:
While sand casting is versatile in accommodating a wide range of part sizes, it may not be suitable for tiny parts with intricate details. The grain size of the sand and the limitations of the casting process can affect the reproduction of fine features accurately. Alternative casting methods, like investment casting or die casting, may be more suitable for such applications.
Conclusion
This comprehensive guide explored the sand casting process and its suitability for manufacturing custom parts. Sand casting offers numerous advantages, including cost-effectiveness, design flexibility, a wide range of compatible alloys, and the potential for sustainable production. Buyers and part design engineers can leverage these benefits to obtain high-quality custom sand casting parts tailored to their specific requirements.
We have discussed the step-by-step process of sand casting, from mold preparation to casting finishing. Each stage plays a crucial role in ensuring the production of accurate and reliable castings. Choosing sand casting materials, such as sand cast aluminum and sand cast steel, allows for versatility and excellent performance in various applications.
Understanding tolerance ranges and mold tolerance is essential in achieving the desired precision and functionality of the cast parts. Buyers can ensure that their custom sand casting parts meet the required specifications by considering factors that affect tolerances and working closely with professional foundries.
While sand casting offers numerous benefits, it is essential to be aware of its limitations. Surface finish and dimensional accuracy may require additional finishing operations, and complex designs can result in longer lead times. Thin-walled parts and tiny parts may pose challenges in the sand casting process. However, by understanding these limitations and exploring alternative casting methods for mass production, buyers can make informed decisions and find the most suitable manufacturing approach for their needs.
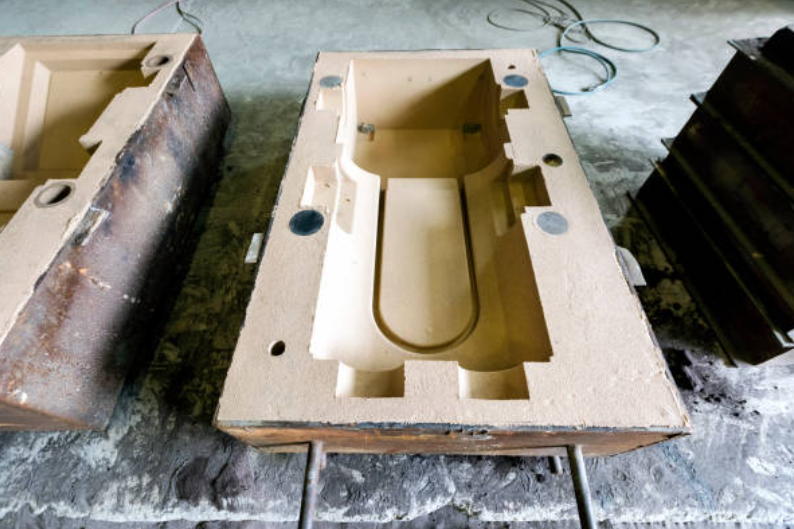

In conclusion, sand casting is a versatile and widely used process for producing custom parts. Its cost-effectiveness, design flexibility, and compatibility with various alloys make it attractive for buyers and part design engineers. High-quality custom sand casting parts can be obtained for various industries and applications by considering the advantages, limitations, and proper techniques.
Summarize the Key Points:
- Sand casting offers cost-effectiveness, design flexibility, and compatibility with various alloys.
- Understanding tolerance ranges and mold tolerance is crucial for achieving precise castings.
- Sand casting has limitations in surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and specific part sizes.
- Alternative casting methods may be considered for mass production requirements.
If you are looking for a reliable sand casting company, contact us for High-Quality Custom Sand Casting Parts.