Custom Metal Parts Production Enhanced by Gravity Castings Techniques
Introduction
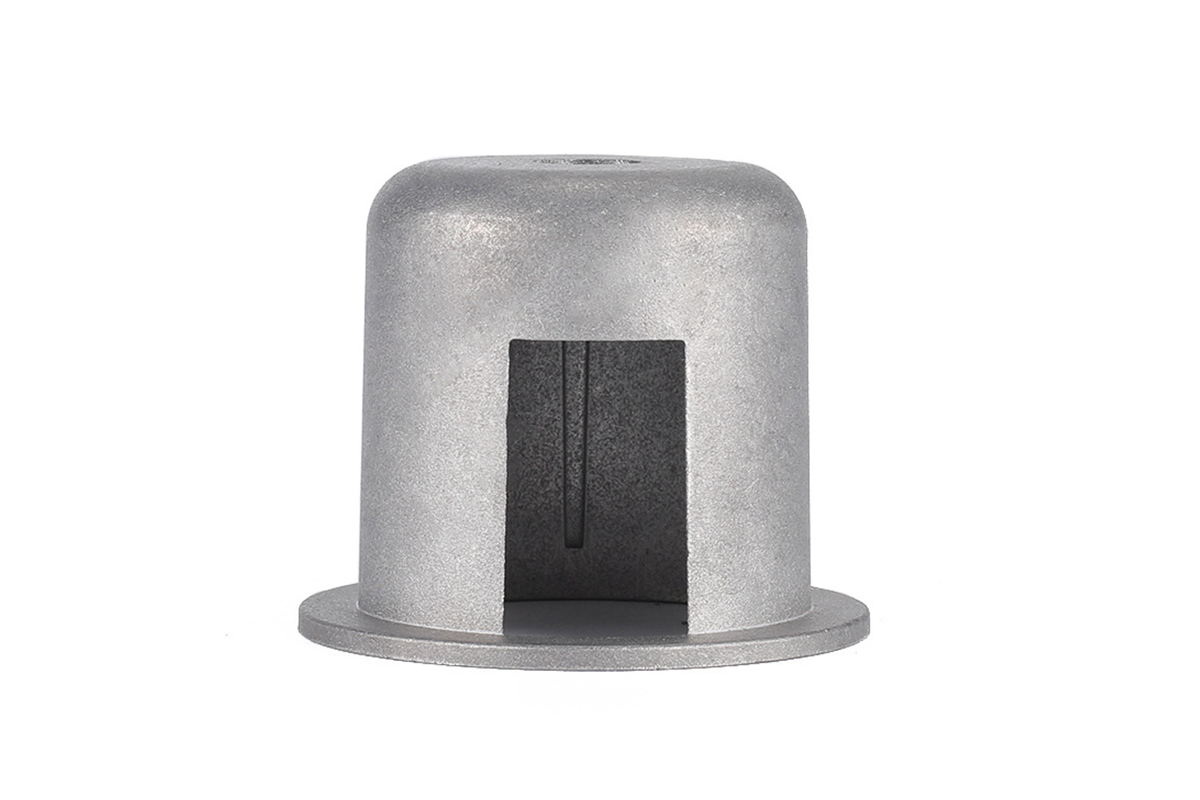
Gravity casting, often known as permanent mold casting, is a versatile metal casting method using gravity-driven mold filling. Leveraging gravity, molten metal fills permanent molds to produce accurate, robust, and high-quality custom metal components essential in automotive, aerospace, marine, electrical, and heavy equipment industries. Its growing popularity comes from effectively balancing accuracy, economy, and performance, making gravity casting ideal for specialized industrial metal applications.
1. Understanding Gravity Casting
Gravity casting involves pouring molten metal directly into permanent molds without external pressure, relying solely on gravity. Compared to temporary molds such as sand molds, permanent steel or iron molds offer superior precision and repeatability.
The process includes several steps:
Preparation of Permanent Mold: Molds are preheated and treated with refractory coatings, ensuring smoother metal flow and part removal.
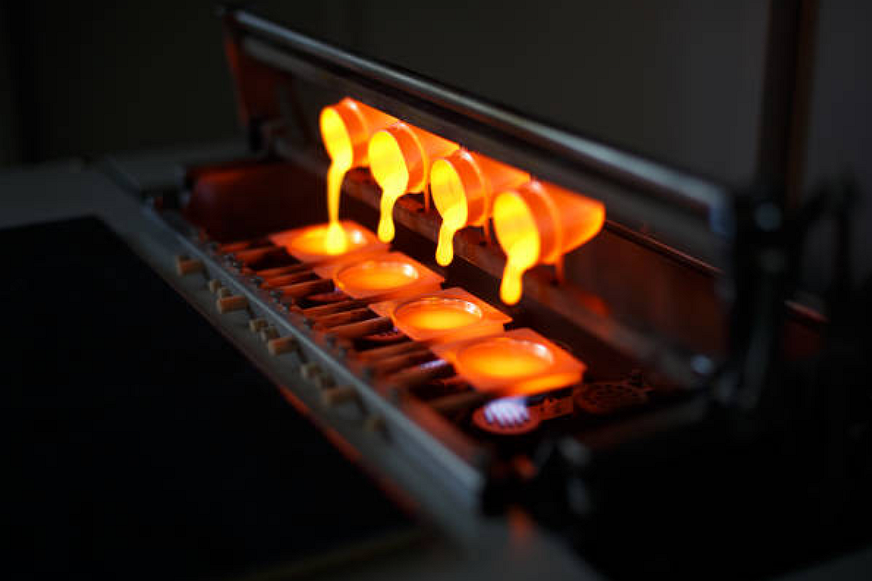
Metal Melting: Melting alloys like aluminum, copper, magnesium, or zinc at controlled furnace temperatures.
Pouring: Gravity-driven molten metal filling of the mold cavity.
Cooling and Solidification: Careful temperature control prevents casting defects during solidification.
Part Removal and Finishing: Cooled parts undergo machining and surface finishing as required.
2. Advantages of Gravity Casting in Custom Metal Parts Production
Gravity casting provides significant advantages for custom metal part production:
High-Dimensional Accuracy and Surface Finish: Permanent molds deliver precisely dimensioned parts requiring minimal post-process machining and polishing.
Enhanced Mechanical Properties: Controlled cooling produces robust components with superior structural integrity.
Cost Efficiency: Economical for small-to-medium production runs due to reusable molds, reducing overall costs compared to methods like investment casting.
Quick Turnaround and Repeatability: Reliable mold reuse ensures consistent production and shorter lead times for custom projects.
3. Common Materials Utilized in Gravity Casting
Specific alloys excel in gravity casting due to advantageous properties:
Aluminum Alloys: Lightweight, durable aluminum is popular in automotive and aerospace manufacturing for its strength-to-weight ratio.
Copper Alloys: Exceptional electrical and thermal conductivity make copper alloys ideal for electrical components and marine hardware.
Magnesium Alloys: Magnesium alloys provide significant weight savings, favored by aerospace and automotive industries.
Zinc Alloys: Zinc alloys offer dimensional stability and excellent castability, perfect for intricate consumer electronics and automotive components.
These materials ensure optimal performance and manufacturing efficiency when gravity cast.
4. Industrial Applications of Gravity Cast Custom Parts
Gravity casting is invaluable across various industrial sectors:
Automotive Components: Critical automotive parts like engine blocks, transmissions, suspension, and brakes achieve required reliability and durability through gravity-cast aluminum alloys.
Aerospace Parts: Aluminum and magnesium gravity castings meet stringent aerospace standards, ensuring safety, lightweight construction, and performance.
Marine Hardware: Highly corrosion-resistant copper and aluminum alloy castings create durable marine fittings, propellers, and engines able to withstand harsh marine environments.
Electrical Components: Gravity-casted copper and zinc alloys produce reliable electrical fittings, connectors, and housings.
Industrial Equipment: Durable valves, pumps, structural supports, and machinery housings benefit from the strength and precision of gravity-casted industrial components.
5. Comparison Between Gravity Casting and Other Casting Methods
Gravity casting’s unique strengths emerge through comparisons:
Gravity Casting vs. Sand Casting:
Sand casting employs disposable sand molds that are suitable for complex geometries but offer lower precision. Conversely, gravity casting yields higher precision, smoother finishes, and improved mechanical strength, which is ideal for medium-volume precision parts.
Gravity Casting vs. Die Casting:
Die casting injects molten metal under pressure, ideal for high-volume precision parts. Without high-pressure equipment, gravity casting is more economical for moderate volumes and thicker, structurally robust components.
Gravity Casting vs. Investment Casting:
Investment casting achieves intricate detail but is more costly with slower production cycles. Gravity casting offers quicker turnarounds, cost-effectiveness, and improved mechanical integrity, making it advantageous for simpler, durable parts.
Gravity casting suits applications demanding durability, moderate complexity, and medium-scale production volumes.
6. Challenges and Solutions in Gravity Casting
Gravity casting faces certain production challenges:
Porosity: Air trapped during casting weakens structures. Effective mold venting, controlled pouring, and optimized temperatures minimize this issue, akin to resolving porosity in aluminum die castings.
Mold Erosion: Molten metal repeatedly interacting with molds can degrade surfaces, impacting accuracy. Applying durable refractory coatings and meticulous mold maintenance extend mold longevity.
Shrinkage: Contraction during cooling leads to structural defects. Strategic gating, riser designs, and precise temperature control effectively mitigate shrinkage issues, similar to addressing shrinkage defects in sand casting processes.
Following best practices and continually refining gravity casting techniques ensure consistently high-quality, defect-free parts.
Conclusion
Gravity casting significantly enhances custom metal parts production through precision, durability, cost-effectiveness, and versatile applications. Addressing industry-specific requirements for accurate, durable components, gravity casting is essential in automotive, aerospace, marine, electrical, and industrial sectors. Proactively managing casting challenges enables manufacturers to leverage gravity casting’s full potential, fueling innovation and efficiency in custom metal part production.
FAQs:
What types of industries use gravity casting for custom metal parts?
How does gravity casting improve part durability?
What materials are best suited for gravity casting?
What are the primary differences between gravity casting and die casting?
How can common defects in gravity casting be minimized?